Catalytic mechanism of a mammalian Rab·RabGAP complex in atomic detail
26-Dec-2012
PNAS, 2012, doi:10.1073/pnas.1214431110, vol. 109, no. 52, 21348–21353 published on 26.12.2012
PNAS, online article
PNAS, online article
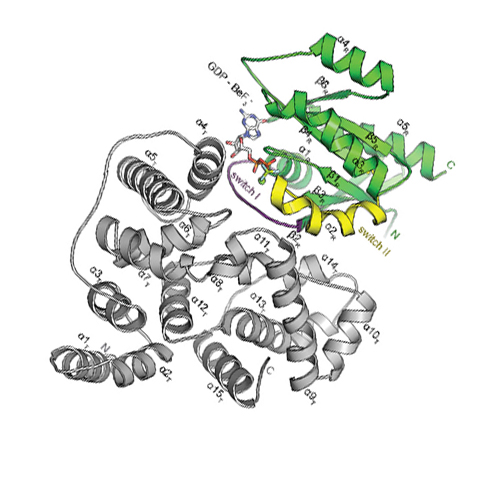
Rab GTPases, key regulators of vesicular transport, hydrolyze GTP very slowly unless assisted by Rab GTPase-activating proteins (RabGAPs). Dysfunction of RabGAPs is involved in many diseases. By combining X-ray structure analysis and time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy we reveal here the detailed molecular reaction mechanism of a complex between human Rab and RabGAP at the highest possible spatiotemporal resolution and in atomic detail. A glutamine residue of Rab proteins (cis-glutamine) that is essential for intrinsic activity is less important in the GAP-activated reaction. During generation of the RabGAP·Rab:GTP complex, there is a rapid conformational change in which the cis-glutamine is replaced by a glutamine from RabGAP (trans-glutamine); this differs from the RasGAP mechanism, where the cis-glutamine is also important for GAP catalysis. However, as in the case of Ras, a trans-arginine is also recruited to complete the active center during this conformational change. In contrast to the RasGAP mechanism, an accumulation of a state in which phosphate is bound is not observed, and bond breakage is the rate-limiting step. The movement of trans-glutamine and trans-arginine into the catalytic site and bond breakage during hydrolysis are monitored in real time. The combination of X-ray structure analysis and time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy provides detailed insight in the catalysis of human Rab GTPases.