The ATP-ase cycle of the endoplamic chaperone GRP94
09-Oct-2007
JBC, 2007, published on 09.10.2007
www.jbc.org, online article
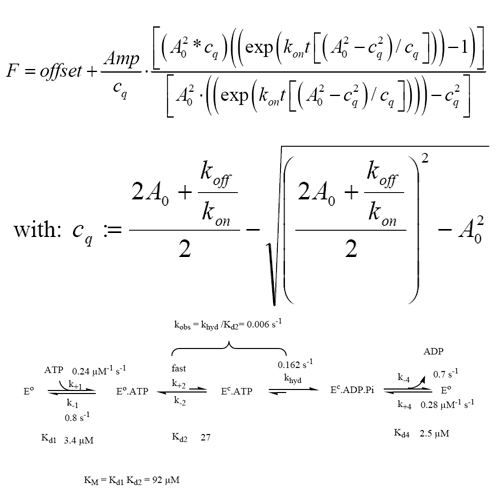
Grp94, the Hsp90 paralogue of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), plays a crucial role in protein secretion. Like cytoplasmic Hsp90, Grp94 is regulated by nucleotide binding to its N-terminal domain. However, the question whether Grp94 hydrolyses ATP was controversial. This sets Grp94 apart from other members of the Hsp90 family where a slow but specific turnover of ATP has been unambiguously established. In this study we aimed at analyzing the nucleotide binding properties and the potential ATPase activity of Grp94. We show here that Grp94 has an ATPase activity comparable to that of yeast Hsp90 with a kcat of 0.36 min-1 at 25°C. Kinetic and equilibrium constants of the partial reactions of the ATPase cycle were determined using transient kinetic methods. Nucleotide binding appears to be tighter compared to other Hsp90s investigated, with dissociation constants (KD) of about 4 μM for ADP, ATP and AMP-PCP. Interestingly, all nucleotides and inhibitors (radicicol, NECA) studied here bind with similar rate constants for association (0.2-0.3 x 106 M-1 s-1). Furthermore, there is a marked difference to cytosolic Hsp90s in that after binding, the ATP molecule does not seem to become trapped by conformational changes in Grp94. Grp94 stays predominantly in the open state concerning the nucleotide binding pocket as evidenced by kinetic analyses. Thus, Grp94 shows mechanistically important differences in the interaction with adenosine nucleotides, but the basic hydrolysis reaction seems to be conserved between cytosolic and endoplasmic members of the Hsp90 family.