Elucidation of the a-Keto-Aldehyde Binding Mechanism: A Lead Structure Motif for Proteasome Inhibition
09-Dec-2010
Angewandte Chemie, 2010, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201005488, published on 19.12.2010
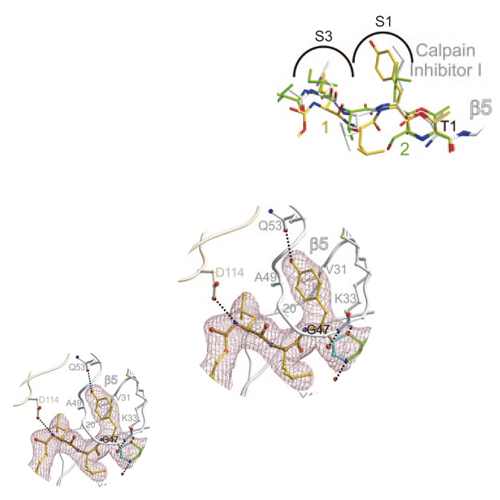
The proteasome's participation in essential biological processes such as stress response, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and antigen presentation has been well established.[1] It is, therefore, not surprising that academia and the pharmaceutical industry have made efforts to develop a range of small synthetic inhibitors against this proteolytic molecular machine (see Scheme SS1 in the Supporting Information for examples).[2] An overall structural comparison of some wellcharacterized inhibitors[3] implies that most of these compounds form a covalent bond with the N-terminal nucleophilic threonine (Thr1)[4] located at the active sites in the two inner heptameric b rings of the 20S proteasome, termed b1, b2, and b5 according to the subunit of their origin.[5]