Characterization of PvuRts1I endonuclease as a tool to investigate genomic 5–hydroxymethylcytosine
04-Mar-2011
Nucl. Acids Res., 2011, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr118, published on 04.03.2011
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
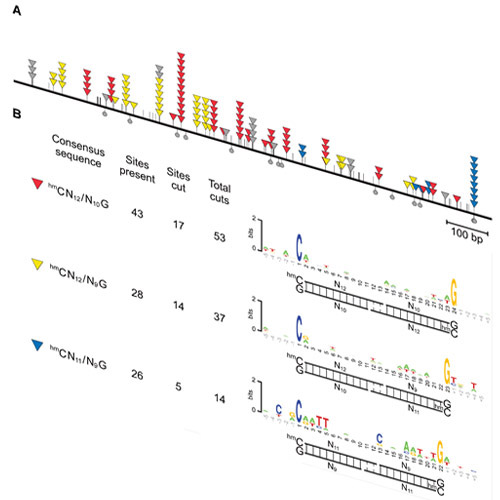
In mammalian genomes a sixth base, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC), is generated by enzymatic oxidation of 5-methylcytosine (mC). This discovery has raised fundamental questions about the functional relevance of hmC in mammalian genomes. Due to their very similar chemical structure, discrimination of the rare hmC against the far more abundant mC is technically challenging and to date no methods for direct sequencing of hmC have been reported. Here, we report on a purified recombinant endonuclease, PvuRts1I, which selectively cleaves hmC-containing sequences. We determined the consensus cleavage site of PvuRts1I as hmCN11–12/N9–10G and show first data on its potential to interrogate hmC patterns in mammalian genomes.