Research Area D - Publications 2016
31-Oct-2016
Pharmaceutical Research, Volume 34, Issue 1, pp 161–174, DOI: 10.1007/s11095-016-2052-8
Pharmaceutical Research, online article

Purpose
Cytosolic delivery of nanobodies for molecular target binding and fluorescent labeling in living cells.
Methods
Fluorescently labeled nanobodies were formulated with sixteen different sequence-defined oligoaminoamides. The delivery of formulated anti-GFP nanobodies into different target protein-containing HeLa cell lines was investigated by flow cytometry ...
24-Oct-2016
Genes & Dev., 30, 2199-2212, doi: 10.1101/gad.284992.116
Genes & Dev., online article

In order to understand whether early epigenetic mechanisms instruct the long-term behavior of neural stem cells (NSCs) and their progeny, we examined Uhrf1 (ubiquitin-like PHD ring finger-1; also known as Np95), as it is highly expressed in NSCs of the developing brain and rapidly down-regulated upon differentiation. Conditional deletion of Uhrf1 in the ...
24-Oct-2016
Nucleic Acids Res., 45 (3): 1114-1129, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw979
Nucleic Acids Res., online article
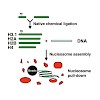
Functional genomic elements are marked by characteristic DNA and histone modification signatures. How combinatorial chromatin modification states are recognized by epigenetic reader proteins and how this is linked to their biological function is largely unknown. Here we provide a detailed molecular analysis of chromatin recognition by the lysine demethylase ...
12-Oct-2016
Mol. Biol. Cell, doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-05-0269
Mol. Biol. Cell, online article
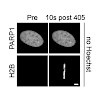
Chromatin relaxation is one of the earliest cellular responses to DNA damage. However, what determines these structural changes, including their ATP requirement, is not well understood. Using live-cell imaging and laser microirradiation to induce DNA lesions, we show that the local chromatin relaxation at DNA damage sites is regulated by PARP1 enzymatic activity. ...
06-Oct-2016
Molecular Cell, Volume 64, Issue 1, p7–9, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.023
Molecular Cell, online article
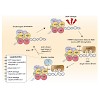
DNA damage induces chemical and structural changes in our chromatin-embedded genome. In a recent issue of Nature Communications, Grundy et al. (2016) identify a role for PARP3 in the repair of single-strand breaks and reveal that PARP3 mono-ADP-ribosylates nucleosomal histone H2B.
05-Oct-2016
Nucl. Acids Res., doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw892
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
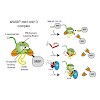
Histone chaperones are proteins that interact with histones to regulate the thermodynamic process of nucleosome assembly. sNASP and ASF1 are conserved histone chaperones that interact with histones H3 and H4 and are found in a multi-chaperoning complex in vivo. Previously we identified a short peptide motif within H3 that binds to the TPR domain of sNASP with ...
27-Sep-2016
NUCLEUS, Pages 1-9, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/19491034.2016.1239000
NUCLEUS, online article
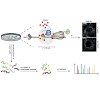
Chromatin structure and function are determined by a plethora of proteins whose genome-wide distribution is typically assessed by immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Here, we developed a novel tool to investigate the local chromatin environment at specific DNA sequences. We combined the programmable DNA binding of dCas9 with the promiscuous biotin ligase BirA* (CasID) to ...
26-Sep-2016
Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, 29 (10): 467-475, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzw037
Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, online article
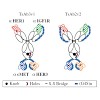
Monoclonal antibody-based targeted tumor therapy has greatly improved treatment options for patients. Antibodies against oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), especially the ErbB receptor family, are prominent examples. However, long-term efficacy of such antibodies is limited by resistance mechanisms. Tumor evasion by a priori or acquired activation of ...
31-Aug-2016
Nature, doi:10.1038/nature19338
Nature, online article

The rules defining which small fraction of related DNA sequences can be selectively bound by a transcription factor are poorly understood. One of the most challenging tasks in DNA recognition is posed by dosage compensation systems that require the distinction between sex chromosomes and autosomes. In Drosophila melanogaster, the male-specific lethal dosage ...
31-Aug-2016
Chem. Commun., 52, 11971-11974, DOI: 10.1039/C6CC05807H
Chem. Commun., online article

N-Acylhomoserine lactones are autoinducers of quorum sensing (QS) in Gram-negative bacteria. We exploit here the role of structurally related β-lactones in the inhibition of Vibrio harveyi bioluminescence and identify a derivative with nanomolar potency. Surprisingly, QS was not affected and combined proteomic/biochemical studies revealed insights into the ...
30-Aug-2016
The Company of Biologists, vol. 143 no. 17, 3154-3167, DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/dev.139634
The Company of Biologists, online article
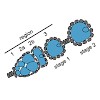
SWR1-type nucleosome remodeling factors replace histone H2A by variants to endow chromatin locally with specialized functionality. In Drosophila melanogaster a single H2A variant, H2A.V, combines functions of mammalian H2A.Z and H2A.X in transcription regulation and the DNA damage response. A major role in H2A.V incorporation for the only SWR1-like enzyme in ...
26-Aug-2016
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 55, Issue 36, Pages 10634–10638, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201604058
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

Mono-ADP-ribosylation is a dynamic posttranslational modification (PTM) with important roles in signaling. Mammalian proteins that recognize or hydrolyze mono-ADP-ribosylated proteins have been described. We report the synthesis of ADP-ribosylated peptides from the proteins histone H2B, RhoA and, HNP-1. An innovative procedure was applied that makes use of ...
24-Aug-2016
Genetics, Vol. 204, 631–644. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.187922
Genetics, online article

Protective mechanisms based on RNA silencing directed against the propagation of transposable elements are highly conserved in eukaryotes. The control of transposable elements is mediated by small non-coding RNAs, which derive from transposon-rich heterochromatic regions that function as small RNA-generating loci. These clusters are transcribed and the precursor ...
12-Aug-2016
PNAS; vol. 113; no.35; E5192-E5201 www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1603435113
PNAS, online article
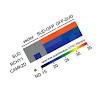
Highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) has developed strategies to inhibit host immune recognition. We identify cellular E3 ubiquitin ligase ring-finger and CHY zinc-finger domain-containing 1 (RCHY1) as an interacting partner of the viral SARS-unique domain (SUD) and papain-like protease (PLpro), and, as a consequence, the ...
04-Aug-2016
Trends in Biochemical Sciences, Volume 41, Issue 9, p736–738, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.07.010
Trends in Biochemical Sciences, online article

Chaperones mediate vital interactions between histones and DNA during chromatin assembly and reorganization. Two recent studies reveal novel substrates for the essential and conserved histone chaperone FAcilitates Chromatin Transcription (FACT). Prendergast et al. show that FACT helps deposit important histone-fold proteins on centromeres. Raj et al. find that ...
25-Jul-2016
Genome Biology, 17:158, DOI 10.1186/s13059-016-1017-x
Genome Biology, online article
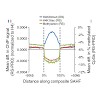
Background
Histone modification H4K20me3 and its methyltransferase SUV420H2 have been implicated in suppression of tumorigenesis. The underlying mechanism is unclear, although H4K20me3 abundance increases during cellular senescence, a stable proliferation arrest and tumor suppressor process, triggered by diverse molecular cues, including activated oncogenes. ...
21-Jul-2016
Chem. Sci., 7, 6995–7001, DOI: 10.1039/c6sc02889f
Chem. Sci., online article

A previously discovered posttranslational modification strategy – arginine rhamnosylation – is essential for elongation factor P (EF-P) dependent rescue of polyproline stalled ribosomes in clinically relevant species such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Neisseria meningitidis. However, almost nothing is known about this new type of N-linked glycosylation. In the ...
07-Jul-2016
BMC Cancer, 16:409, DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2471-2
BMC Cancer, online article
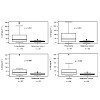
Background
Interleukin-22 (IL-22) is involved in lung diseases such as pneumonia, asthma and lung cancer. Lavage mirrors the local environment, and may provide insights into the presence and role of IL-22 in patients.
Methods
Bronchoscopic lavage (BL) samples (n = 195, including bronchoalveolar lavage and bronchial washings) were analysed for IL-22 using an ...
28-Jun-2016
Cell Reports, Volume 16, Issue 1, p48–55, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.073
Cell Reports, online article

During class switch recombination (CSR), B cells replace the Igh Cμ or δ exons with another downstream constant region exon (CH), altering the antibody isotype. CSR occurs through the introduction of AID-mediated double-strand breaks (DSBs) in switch regions and subsequent ligation of broken ends. Here, we developed an assay to investigate the dynamics of DSB ...
22-Jun-2016
Nature, 534, 714–718, doi:10.1038/nature18312
Nature, online article
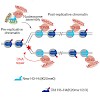
After DNA replication, chromosomal processes including DNA repair and transcription take place in the context of sister chromatids. While cell cycle regulation can guide these processes globally, mechanisms to distinguish pre- and post-replicative states locally remain unknown. Here we reveal that new histones incorporated during DNA replication provide a ...
17-Jun-2016
The Company of Biologists, 143: 1788-1799; doi: 10.1242/dev.130203
The Company of Biologists, online article

The H3K9me3-specific histone methyltransferase Setdb1 impacts on transcriptional regulation by repressing both developmental genes and retrotransposons. How impaired retrotransposon silencing may lead to developmental phenotypes is currently unclear. Here, we show that loss of Setdb1 in pro-B cells completely abrogates B cell development. In pro-B cells, Setdb1 ...
16-Jun-2016
Cell Reports, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.081
Cell Reports, online article

Cells have evolved diverse mechanisms that maintain intracellular homeostasis in fluctuating environments. In bacteria, control is often exerted by bifunctional receptors acting as both kinase and phosphatase to regulate gene expression, a design known to provide robustness against noise. Yet how such antagonistic enzymatic activities are balanced as a function ...
06-Jun-2016
Cell PressTrends inBiochemicalSciences, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.05.008
Cell Press, online article

Loss of cellular homeostasis during aging results in altered tissue functions and leads to a general decline in fitness and, ultimately, death. As animals age, the control of gene expression, which is orchestrated by multiple epigenetic factors, degenerates. In parallel, metabolic activity and mitochondrial protein acetylation levels also change. These two ...
06-Jun-2016
Trends in Biochemical Sciences, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.05.010
Trends in Biochemical Sciences, online article

Low-complexity (LC) domains regulate the aggregation and phase transition of proteins in a modification-dependent manner. The study of LC domain modifications has now become feasible, as shown by genetic variants of the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) that provide access to the type and position of modifications of a LC domain by mass ...
06-Jun-2016
Scientific Reports, 6, Article number: 27401, doi:10.1038/srep27401
Scientific Reports, online article
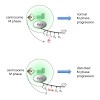
Dynamic phosphorylation of Tyr1-Ser2-Pro3-Thr4-Ser5-Pro6-Ser7 heptad-repeats in the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the large subunit coordinates progression of RNA polymerase (Pol) II through the transcription cycle. Here, we describe an M phase-specific form of Pol II phosphorylated at Thr4, but not at Tyr1, Ser2, Ser5, and Ser7 residues. Thr4 phosphorylated Pol II ...
31-May-2016
OncoImmunology, Volume 5, Issue 7, e1189051, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2016.1189051
OncoImmunology, online article

Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) agonists are potent immune stimulants able to overcome cancer-associated immune suppression. Due to dose-limiting systemic toxicities, only the topically applied TLR7 agonist (imiquimod) has been approved for therapy of skin tumors. There is a need for TLR7-activating compounds with equivalent efficacy but less toxicity. SC1, a novel ...
23-May-2016
PLoS ONE, 11(5): e0156010, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0156010
PLoS ONE, online article

Phages are bacteria targeting viruses and represent the most abundant biological entities on earth. Marine environments are exceptionally rich in bacteriophages, harboring a total of 4x1030 viruses. Nevertheless, marine phages remain poorly characterized. Here we describe the identification of intact prophage sequences in the genome of the marine ...
23-May-2016
Journal of Immunology Research, Volume 2016, Article ID 3576028, 11 pages, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3576028
Journal of Immunology Research, online article
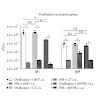
Purified protein vaccines often require adjuvants for efficient stimulation of immune responses. There is no licensed mucosal adjuvant on the market to adequately boost the immune response to purified antigens for intranasal applications in humans. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMV) are attractive candidates potentially combining antigenic and adjuvant ...
03-May-2016
Neuroepigenetics, Volume 6, Pages 10–25, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nepig.2016.04.001
Neuroepigenetics, online article
Neural stem progenitor cells (NSPCs) in the human subventricular zone (SVZ) potentially contribute to lifelong neurogenesis, yet subtypes of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) contain NSPC signatures that highlight the importance of cell fate regulation. Among numerous regulatory mechanisms, the posttranslational methylations onto histone tails are crucial regulator ...
02-May-2016
JCB, vol. 213, no. 3, 305-314, doi: 10.1083/jcb.201601089
JCB, online article
Sorting and export of transmembrane cargoes and lysosomal hydrolases at the trans-Golgi network (TGN) are well understood. However, elucidation of the mechanism by which secretory cargoes are segregated for their release into the extracellular space remains a challenge. We have previously demonstrated that, in a reaction that requires Ca2+, the soluble ...
25-Apr-2016
OncoImmunology, Volume 5, Issue 9, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2016.1175794
OncoImmunology, online article
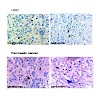
In cancer patients, immunosuppression through regulatory T cells (Treg) is a crucial component of tumor immune evasion and contributes to disease progression. Tumor-infiltrating Treg in particular suppress local effector T cell responses and are associated with poor prognosis in tumors such as human pancreatic cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The ...
16-Apr-2016
Biotechnology Progress, Volume 32, Issue 3, Pages 776–786, DOI: 10.1002/btpr.2271
Biotechnology Progress, online article

Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO) are widely used in the production of glycosylated therapeutic proteins such as antibodies. During expansion and maintenance, CHO cell lines are prone to production instability, which may be caused by promoter silencing, loss of transgene copies, or post-transcriptional effects. Silencing of recombinant genes may be accompanied by ...
07-Apr-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 11231, doi:10.1038/ncomms11231

Since the pioneering proposal of the replicon model of DNA replication 50 years ago, the predicted replicons have not been identified and quantified at the cellular level. Here, we combine conventional and super-resolution microscopy of replication sites in live and fixed cells with computational image analysis. We complement these data with genome size ...
24-Mar-2016
Bioscience Reports, 36, e00326, DOI: 10.1042/BSR20160069
Bioscience Reports, online article

Most bacterial response regulators make contact with DNA through a recognition α-helix in their DNA-binding domains. An emerging class of response regulators interacts with DNA via a relatively novel type of binding domain, called the LytTR domain, which is mainly composed of beta-strands. YpdB belongs to this latter class, is part of a nutrient-sensing network ...
17-Mar-2016
Medical Image Analysis, Volume 32, Pages 18–31, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2016.03.001
Medical Image Analysis, online article

The genome is partitioned into regions of euchromatin and heterochromatin. The organization of heterochromatin is important for the regulation of cellular processes such as chromosome segregation and gene silencing, and their misregulation is linked to cancer and other diseases. We present a model-based approach for automatic 3D segmentation and 3D shape analysis ...
16-Feb-2016
Plos One, 11 (2), DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0149187

Two-component systems are the major means by which bacteria couple adaptation to environmental changes. All utilize a phosphorylation cascade from a histidine kinase to a response regulator, and some also employ an accessory protein. The system-wide signaling fidelity of two-component systems is based on preferential binding between the signaling proteins. ...
15-Feb-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 10754, doi:10.1038/ncomms10754
Aneuploidy is a hallmark of cancer and underlies genetic disorders characterized by severe developmental defects, yet the molecular mechanisms explaining its effects on cellular physiology remain elusive. Here we show, using a series of human cells with defined aneuploid karyotypes, that gain of a single chromosome increases genomic instability. Next-generation ...
15-Feb-2016
Biochemical Pharmacology, Volume 102, 130–140, Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2015.12.010
Biochemical Pharmacology, online article
Lysine acetylations are reversible posttranslational modifications of histone and non-histone proteins that play important regulatory roles in signal transduction cascades and gene expression. Lysine acetylations are regulated by histone acetyltransferases as writers and histone deacetylases as erasers. Because of their role in signal transduction cascades, these ...
02-Feb-2016
Developmental Biology, Volume 411, Issue 2, Pages 217–230, doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.01.039

The Chromatin Accessibility Complex (CHRAC) consists of the ATPase ISWI, the large ACF1 subunit and a pair of small histone-like proteins, CHRAC-14/16. CHRAC is a prototypical nucleosome sliding factor that mobilizes nucleosomes to improve the regularity and integrity of the chromatin fiber. This may facilitate the formation of repressive chromatin. Expression of ...
27-Jan-2016
Cell Systems, Volume 2, Issue 1, p49–58, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2016.01.002

Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are pivotal to cellular information processing, but how combinatorial PTM patterns (“motifs”) are set remains elusive. We develop a computational framework, which we provide as open source code, to investigate the design principles generating the combinatorial acetylation patterns on histone H4 in Drosophila melanogaster. ...
25-Jan-2016
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, vol. 15, no. 3, 945-959, doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.053553
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, online article

The structure of chromatin is critical for many aspects of cellular physiology and is considered to be the primary medium to store epigenetic information. It is defined by the histone molecules that constitute the nucleosome, the positioning of the nucleosomes along the DNA and the non-histone proteins that associate with it. These factors help
to establish and ...
22-Jan-2016
Haematologica May 2016,: vol. 101, no. 5 e168-e172; doi:10.3324/haematol.2015.139980
Haematologica, online article
Research efforts to establish therapeutic modalities for treating sickle cell disease (SCD) and β-thalassemia have been hindered by our incomplete understanding of the developmental regulation of human β-like globin gene expression. It has been demonstrated that increased embryonic globin (ε-globin) gene expression, similar to fetal globin (γ-globin), can ...
21-Jan-2016
Molecular Cell, Volume 61, Issue 2, Pages 305–314 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.12.003

The carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) consists of heptad repeats with the consensus motif Y1-S2-P3-T4-S5-P6-S7. Dynamic phosphorylation of the CTD coordinates Pol II progression through the transcription cycle. Here, we use genetic and mass spectrometric approaches to directly detect and map phosphosites along the entire CTD. We confirm ...
18-Jan-2016
EMBO reports, DOI: 10.15252/embr.201541132
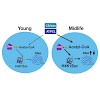
Old age is associated with a progressive decline of mitochondrial function and changes in nuclear chromatin. However, little is known about how metabolic activity and epigenetic modifications change as organisms reach their midlife. Here, we assessed how cellular metabolism and protein acetylation change during early aging in Drosophila melanogaster. Contrary to ...










