Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 links RNA Polymerase II transcription to processing of ribosomal RNA
06-Jun-2013
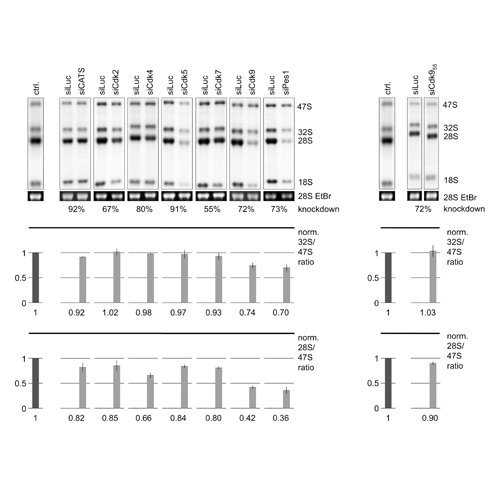
Ribosome biogenesis is a process required for cellular growth and proliferation. Processing of ribosomal (r)RNA is highly sensitive to flavopiridol, a specific inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (Cdk9). Cdk9 has been characterised as the catalytic subunit of the positive transcription elongation factor-b (P-TEFb) of RNA polymerase (RNAP)II. Here we studied the connection between RNAPII transcription and rRNA processing. We show that inhibition of RNAPII activity by α-amanitin specifically blocks processing of rRNA. The block is characterised by accumulation of 3' extended unprocessed 47S rRNAs and the entire inhibition of other 47S rRNA specific processing steps. The transcription rate of rRNA is moderately reduced after inhibition of Cdk9, suggesting that defective 3' processing of rRNA negatively feeds back on RNAPI transcription. Knockdown of Cdk9 caused a strong reduction of the levels of RNAPII transcribed U8 small nucleolar (sno)RNA, which is essential for 3' rRNA processing in mammalian cells. Our data demonstrate a pivotal role of Cdk9 activity for coupling of RNAPII transcription with snoRNA production and rRNA processing.