Synergy between CD26/DPP-IV Inhibition and G-CSF Improves Cardiac Function after Acute Myocardial Infarction
03-Apr-2009
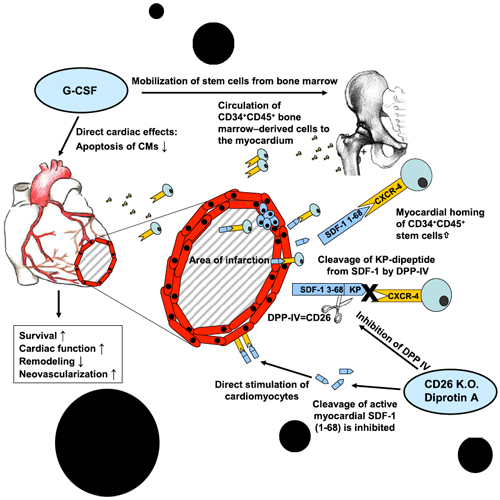
Ischemic cardiomyopathy is one of the main causes of death, which may be prevented by stem cell-based therapies. SDF-1a is the major chemokine attracting stem cells to the heart. Since SDF-1a is cleaved and inactivated by CD26/dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP-IV), we established a therapeutic concept— applicable to ischemic disorders in general—by combining genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of DPP-IV with G-CSF-mediated stem cell mobilization after myocardial infarction in mice. This approach leads to (1) decreased myocardial DPP-IV activity, (2) increased myocardial homing of circulating CXCR-4+ stem cells, (3) reduced cardiac remodeling, and (4) improved heart function and survival. Indeed, CD26 depletion promoted posttranslational stabilization of active SDF-1a in heart lysates and preserved the cardiac SDF-1-CXCR4 homing axis. Therefore, we propose pharmacological DPP-IV inhibition and G-CSF-based stem cell mobilization as a therapeutic concept for future stem cell trials after myocardial infarction.