Research Area C - Publications 2012
14-Nov-2013

The general transcription factor (TF) IIB is required for RNA polymerase (Pol) II initiation and extends with its B-reader element into the Pol II active centre cleft. Low-resolution structures of the Pol II–TFIIB complex indicated how TFIIB functions in DNA recruitment, but they lacked nucleic acids and half of the B-reader, leaving other TFIIB functions ...
13-Dec-2012
Science, online article
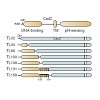
Translation elongation factor P (EF-P) is critical for virulence in bacteria. EF-P is present in all bacteria and orthologous to archaeal and eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, yet the biological function has so far remained enigmatic. Here, we demonstrate that EF-P is an elongation factor that enhances translation of polyproline-containing proteins: In the absence ...
12-Dec-2012
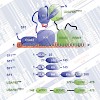
Investigating the different functions of distinct surface receptors is essential to understand the complex interactions between cells and their extracellular environment. Cells use specific transmembrane receptors of the integrin family to anchor and respond to extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. In doing so, integrins are capable of regulating cell migration, ...
Promiscuous behaviour of archaeal ribosomal proteins: Implications for eukaryotic ribosome evolution
06-Dec-2012
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
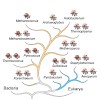
In all living cells, protein synthesis occurs on ribonucleoprotein particles called ribosomes. Molecular models have been reported for complete bacterial 70S and eukaryotic 80S ribosomes; however, only molecular models of large 50S subunits have been reported for archaea. Here, we present a complete molecular model for the Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome based ...
21-Nov-2012
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Recognition of the 30-splice site is a key step in premRNA splicing and accomplished by a dynamic complex comprising splicing factor 1 (SF1) and the U2 snRNP auxiliary factor 65-kDa subunit (U2AF65). Both proteins mediate protein–protein and protein–RNA interactions for cooperative RNA-binding during spliceosome assembly. Here, we report the solution structure of ...
19-Nov-2012
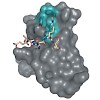
N-Methylation is one of the simplest chemical modifications often occurring in peptides and proteins of prokaryotes and higher eukaryotes. Over years of evolution, nature has employed N-methylation of peptides as an ingenious technique to modulate biological function, often as a mode of survival through the production of antibiotics. This small structural change ...
24-Oct-2012
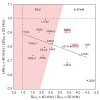
The 1H dipolar network, which is the major obstacle for applying proton detection in the solid-state, can be reduced by deuteration, employing the RAP (Reduced Adjoining Protonation) labeling scheme, which yields random protonation at non-exchangeable sites. We present here a systematic study on the optimal degree of random sidechain protonation in RAP samples as ...
01-Oct-2012
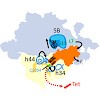
Ribosome protection proteins (RPPs) confer tetracycline resistance by binding to the ribosome and chasing the drug from its binding site. The current model for the mechanism of action of RPPs proposes that drug release is indirect and achieved via conformational changes within the drug-binding site induced upon binding of the RPP to the ribosome. Here we report a ...
24-Aug-2012

The green tea compound epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) neurotoxicity. Solution-state NMR allows probing initial EGCG–Aβ interactions. We show that EGCG-induced Aβ oligomers adopt a well-defined structure and are amenable for magic angle spinning solid-state NMR investigations. We find that EGCG interferes with ...
06-Aug-2012
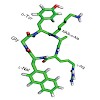
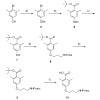
There can be only one: Using a peptoid motif obtained by shifting the arginine side chain of a pentapeptide previously developed by Fujii et al. to the neighboring nitrogen atom restricts the conformational freedom and yields a conformationally homogeneous peptide (see picture) with a 100-fold higher binding affinity to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in the ...
24-Jul-2012
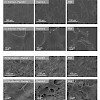
It is well known that functionalization of surfaces with cell adhesive peptides mimicking the integrin binding motif of extracellular matrix proteins is a feasible approach to improve osseointegration of implant materials. Also, modification of the surface properties of the material (e.g., roughness) strongly influences cell behavior. However, these two ...
29-Jun-2012
In different phases of the transcription cycle, RNA polymerase (Pol) II recruits various factors via its C-terminal domain (CTD), which consists of conserved heptapeptide repeats with the sequence Tyr1-Ser2-Pro3-Thr4-Ser5-Pro6-Ser7. We show that the CTD of transcribing yeast Pol II is phosphorylated at Tyr1, in addition to Ser2, Thr4, Ser5, and Ser7. Tyr1 ...
27-Jun-2012
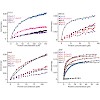
Insufficient oral bioavailability is considered as a key limitation for the widespread development of peptides as therapeutics. While the oral bioavailability of small organic compounds is often estimated from simple rules, similar rules do not apply to peptides, and even the high oral bioavailability that is described for a small number of peptides is not well ...
25-Jun-2012
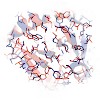
We have developed an approach for determining NMR structures of proteins over 20 kDa that utilizes sparse distance restraints obtained using transverse relaxation optimized spectroscopy experiments on perdeuterated samples to guide RASREC Rosetta NMR structure calculations. The method was tested on 11 proteins ranging from 15 to 40 kDa, seven of which were ...
22-Jun-2012

Due to the biocompatibility and biodegradability as well as the mechanical properties of the fibers, spider silk has become an attractive material for researchers regarding biomedical applications. In this study, the engineered recombinant spider silk protein eADF4(C16) was modified with the integrin recognition sequence RGD by a genetic (fusing the amino acid ...
22-Jun-2012

We provide here a molecular movie that captures key aspects of RNA polymerase II initiation and elongation. To create the movie, we combined structural snapshots of the initiation-elongation transition and of elongation, including nucleotide addition, translocation, pausing, proofreading, backtracking, arrest, reactivation, and inhibition. The movie reveals open ...
21-Jun-2012
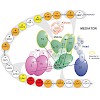
The Mediator is a highly conserved, large multiprotein complex that is involved essentially in the regulation of eukaryotic mRNA transcription. It acts as a general transcription factor by integrating regulatory signals from gene-specific activators or repressors to the RNA Polymerase II. The internal network of interactions between Mediator subunits that conveys ...
20-Jun-2012
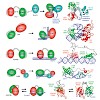
Protein–RNA interactions play essential roles in gene regulation and RNA metabolism. While high-resolution structures have revealed principles of RNA recognition by individual RNA binding domains (RBDs), the presence of multiple RBDs in many eukaryotic proteins suggests additional modes of RNA recognition by combination and cooperation of these interactions. ...
17-Jun-2012
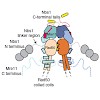
The Mre11–Rad50–Nbs1 (MRN) complex tethers, processes and signals DNA double-strand breaks, promoting genomic stability. To understand the functional architecture of MRN, we determined the crystal structures of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Mre11 dimeric catalytic domain alone and in complex with a fragment of Nbs1. Two Nbs1 subunits stretch around the outside of ...
17-Jun-2012

Lys34 of the conserved translation elongation factor P (EF-P) is post-translationally lysinylated by YjeK and YjeA—a modification that is critical for bacterial virulence. Here we show that the currently accepted Escherichia coli EF-P modification pathway is incomplete and lacks a final hydroxylation step mediated by YfcM, an enzyme distinct from deoxyhypusine ...
09-May-2012

The 3 life scientists Ulrike Gaul, Andreas Ladurner and Michael Sattler from CIPSM were today recognised by EMBO for their excellence in research. EMBO elects new members annually on the basis of scientific excellence. The selected researchers will help shape the direction of the life sciences in Europe and beyond by their involvement with the activities of the ...
08-May-2012
Aggregation of monomeric amyloid beta peptides (ABeta) into soluble oligomers and insoluble fibrils is one of the major pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer_s disease (AD). In the past few years, magic angle spinning (MAS) solid-state NMR spectroscopy has enabled considerable progress in the structural characterization of amyloid aggregates, and a number of ...
16-Apr-2012
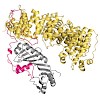
Swi2/Snf2 (switch/sucrose non-fermentable) enzymes form a large and diverse class of proteins and multiprotein assemblies that remodel nucleic acid:protein complexes, using the energy of ATP hydrolysis. The core Swi2/Snf2 type ATPase domain belongs to the ‘helicase and NTP driven nucleic acid translocase’ superfamily 2 (SF2). It serves as a motor that ...
13-Apr-2012
UV-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) in the template DNA strand stall transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). If the nucleotide excision repair machinery does not promptly remove the CPDs, stalled Pol II creates a roadblock for DNA replication and subsequent rounds of transcription. Here we present evidence that Pol II has an intrinsic ...
05-Apr-2012
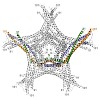
The Ska complex is an essential mitotic component required for accurate cell division in human cells. It is composed of three subunits that function together to establish stable kinetochore-microtubule interactions in concert with the Ndc80 network. We show that the structure of the Ska core complex is a W-shaped dimer of coiled coils, formed by intertwined ...
30-Mar-2012
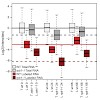
To monitor eukaryotic mRNA metabolism, we developed comparative Dynamic Transcriptome Analysis (cDTA). cDTA provides absolute rates of mRNA synthesis and decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc) cells with the use of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) as internal standard. cDTA uses non-perturbing metabolic labeling that supersedes conventional methods for mRNA ...
26-Mar-2012
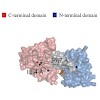
In a recent study we described the second periplasmic loop P2 of the transmembrane protein MalF (MalF-P2) of the maltose ATP-binding cassette transporter (MalFGK2-E) as an important element in the recognition of substrate by the maltose-binding protein MalE. In this study, we focus on MalE and find that MalE undergoes a structural rearrangement after addition of ...
15-Mar-2012
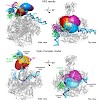
The open promoter complex (OC) is a central intermediate during transcription initiation that contains a DNA bubble. Here, we employ single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer experiments and Nano-Positioning System analysis to determine the three-dimensional architecture of a minimal OC consisting of promoter DNA, including a TATA box and an 11-nucleotide ...
06-Mar-2012

RNA polymerase (Pol) I contains a 10-subunit catalytic core that is related to the core of Pol II and includes subunit A12.2. In addition, Pol I contains the heterodimeric subcomplexes A14/43 and A49/34.5, which are related to the Pol II subcomplex Rpb4/7 and the Pol II initiation factor TFIIF, respectively. Here we used lysine-lysine crosslinking, mass ...
03-Mar-2012
Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging, 2012, DOI 10.1007/s00259-011-2028-1, Volume 39, Issue 1 Supplement, pp 126-138 published on 03.03.2012
Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging, online article
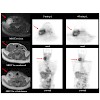
Imaging of angiogenesis has become increasingly important with the rising use of targeted antiangiogenic therapies like bevacizumab (Avastin). Non-invasive assessment of angiogenic activity is in this respect interesting, e.g. for response assessment of such targeted antiangiogenic therapies. One promising approach of angiogenesis imaging is imaging of specific ...
23-Feb-2012
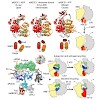
Ribosome-driven protein biosynthesis is comprised of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination and recycling. In bacteria, ribosome recycling requires ribosome recycling factor and elongation factor G, and several structures of bacterial recycling complexes have been determined. In the eukaryotic and archaeal kingdoms, however, recycling involves the ...
23-Feb-2012
In the forthcoming era of cancer gene therapy, efforts will be devoted to the development of new efficient and non-toxic gene delivery vectors. In this regard, the use of Fmoc/Boc-protected oligo(ethane amino)acids as building blocks for solid-phase-supported assembly represents a novel promising approach towards fully controlled syntheses of effective gene ...
23-Feb-2012
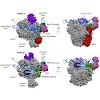
Recent studies of the three eukaryotic transcription machineries revealed that all initiation complexes share a conserved core. This core consists of the RNA polymerase (I, II, or III), the TATA box-binding protein (TBP), and transcription factors TFIIB, TFIIE, and TFIIF (for Pol II) or proteins structurally and functionally related to parts of these factors (for ...
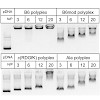
21-Feb-2012
TP-434 is a novel, broad-spectrum fluorocycline antibiotic with activity against bacteria expressing major antibiotic resistance mechanisms, including tetracycline-specific efflux and ribosomal protection. The mechanism of action of TP-434 was assessed using both cell-based and in vitro assays. In Escherichia coli cells expressing recombinant tetracycline ...
15-Feb-2012
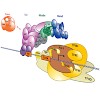
Gene transcription by RNA polymerase II requires the multiprotein coactivator complex Mediator. Mediator was identified two decades ago, but its molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood, because structural studies are hampered by its large size, modularity, and flexibility. Here we collect all available structural data on Mediator and discuss their ...
10-Feb-2012

One of the earliest steps in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing involves binding of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor (U2AF) 65 KDa subunit to the polypyrimidine (Py) tract and of the 35 KDa subunit to the invariant AG dinucleotide at the intron 3′ end. Here we use in vitro and in vivo depletion, as well as reconstitution assays using purified components, to identify hnRNP A1 as ...
09-Feb-2012
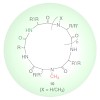
This protocol presents a detailed description of the synthesis of N-methylated cyclic peptides. N-methylation is a powerful technique to modulate the physicochemical properties of peptides by introducing one or more methyl groups into the peptidic amide bonds. Together with peptide cyclization, this procedure confers unprecedented pharmacokinetic properties to ...
01-Feb-2012
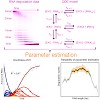
RNA exosomes are large multi-subunit protein complexes involved in controlled and processive 3' to 5' RNA degradation. Exosomes form large molecular chambers and harbor multiple nuclease sites as well as RNA binding regions. This makes a quantitative kinetic analysis of RNA degradation with reliable parameter and error estimates challenging. For instance, recent ...
09-Jan-2012

Structural information is key for understanding biological processes. Insoluble proteins, like membrane proteins and amyloid fibrils, are a large class of proteins that are underrepresented in the protein data bank (PDB). As of today, only 7% of all entries in the PDB refer to either a membrane protein or an amyloid fibril structure (membrane protein: 4994 ...
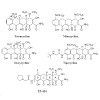
09-Jan-2012
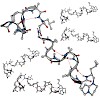
The efrapeptin family of peptide antibiotics produced by the fungus Tolypocladium niveum, and the neo-efrapeptins from the fungus Geotrichum candidumare inhibitors of F1-ATPase with promising antitumor, antimalaria, and insecticidal activity. They are rich in Cα-dialkyl amino acids (Aib, Iva, Acc) and contain one β-alanine and several pipecolic acid residues. The ...
08-Jan-2012
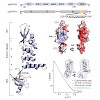
Chromodomains typically recruit protein complexes to chromatin and read the epigenetic histone code by recognizing lysine methylation in histone tails. We report the crystal structure of the chloroplast signal recognition particle (cpSRP) core from Arabidopsis thaliana, with the cpSRP54 tail comprising an arginine-rich motif bound to the second chromodomain of ...
06-Jan-2012
The EMBO Journal, online article

Sti1/Hop is a modular protein required for the transfer of client proteins from the Hsp70 to the Hsp90 chaperone system in eukaryotes. It binds Hsp70 and Hsp90 simultaneously via TPR (tetratricopeptide repeat) domains. Sti1/Hop contains three TPR domains (TPR1, TPR2A and TPR2B) and two domains of unknown structure (DP1 and DP2). We show that TPR2A is the high ...
06-Jan-2012

The human small heat-shock protein alphaB-crystallin (alphaB) rescues misfolded proteins from irreversible aggregation during cellular stress. Binding of Cu(II) was shown to modulate the oligomeric architecture and the chaperone activity of alphaB. However, the mechanistic basis of this stimulation is so far not understood. We provide here first structural ...
06-Jan-2012

Lamin B receptor (LBR) is a polytopic protein of the nuclear envelope thought to connect the inner nuclear membrane with the underlying nuclear lamina and peripheral heterochromatin. To better understand the function of this protein, we have examined in detail its nucleoplasmic region, which is predicted to harbor a Tudor domain (LBR-TD). Structural analysis by ...
05-Jan-2012
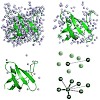
High resolution proton spectra are obtained in MAS solid-state NMR in case samples are prepared using perdeuterated protein and D2O in the recrystallization buffer. Deuteration reduces drastically 1H, 1H dipolar interactions and allows to obtain amide proton line widths on the order of 20 Hz. Similarly, high-resolution proton spectra of aliphatic groups can be ...
01-Jan-2012
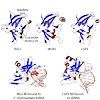
The innate immune system is a first layer of defense against infection by pathogens. It responds to pathogens by activating host defense mechanisms via interferon and inflammatory cytokine expression. Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are sensed by specific pattern recognition receptors. Among those, the ATP dependent helicase related RIG-I like ...










