News 2011
15-Jul-2012

Twenty years ago, fluorescence measurements at low concentrations were difficult due to the weak fluorescence signal and intrinsic fluctuations of the sample. With the development of FCS and its implementation on a confocal microscope, it is possible to use the inherent fluctuations to gain information over the concentration, molecular brightness, microscopic ...
26-Dec-2011
The diffusion dynamics of terrylene diimide (TDI) dye molecules and dye-labeled double-strand DNA were studied in micrometer long silica filaments containing collinear, oriented mesopores using single molecule fluorescence microscopy. TDI was used as a stable and hydrophobic probe molecule for single molecule structural analysis. We used template-free mesoporous ...
22-Dec-2011
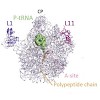
The peptidyltransferase center of the large ribosomal subunit is responsible for catalyzing peptide bonds. This active site is the target of a variety of diverse antibiotics, many of which are used clinically. The past decade has seen a plethora of structures of antibiotics in complex with the large ribosomal subunit, providing unprecedented insight into the ...
20-Dec-2011

The molecular chaperone αB-crystallin, the major player in maintaining the transparency of the eye lens, prevents stress-damaged and aging lens proteins from aggregation. In nonlenticular cells, it is involved in various neurological diseases, diabetes, and cancer. Given its structural plasticity and dynamics, structure analysis of αB-crystallin presented ...
19-Dec-2011
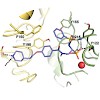
Intervention in integrin-mediated cell adhesion and integrin signaling pathways is an ongoing area of research in medicinal chemistry and drug development. One key element in integrin–ligand interaction is the coordination of the bivalent cation at the metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS) by a carboxylic acid function, a consistent feature of all integrin ...
16-Dec-2011

Photochromic channel blockers provide a conceptually simple and convenient way to modulate neuronal activity with light. We have recently described a family of azobenzenes that function as tonic blockers of Kv channels but require UV-A light to unblock and need to be actively switched by toggling between two different wavelengths. We now introduce red-shifted ...
15-Dec-2011

Labeling of RGD peptides with near-infrared fluorophores yields optical probes for noninvasive imaging of tumors overexpressing alpha-v-beta3 integrins. An important prerequisite for optimum detection sensitivity in vivo is strongly absorbing and highly emissive probes with a known fluorescence lifetime. The RGD-Cy5.5 optical probe was derived by coupling Cy5.5 ...
15-Dec-2011
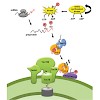
Import of nuclear encoded proteins into chloroplast is an essential and well-regulated mechanism. The cytosolic kinases STY8, STY17 and STY46 have been shown to phosphorylate chloroplast preprotein transit peptides advantaging the binding of a 14-3-3 dimer. Analyses of sty8 sty17 sty46 mutant plants revealed a role for the kinases in chloroplast differentiation, ...
13-Dec-2011
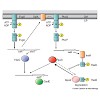
Two-component systems, composed of a histidine kinase (HK) and a response regulator (RR), are the major signal transduction devices in bacteria. Originally it was thought that these two components function as linear, phosphorylationdriven stimulus–response system. Here, we will review how accessory proteins are employed by HKs and RRs to mediate signal ...
13-Dec-2011

We present a strategy for rapidly gaining structural information about a protein from crosslinks formed by genetically encoded unnatural amino acids. We applied it to ISWI, a chromatin remodeling enzyme involved in chromatin assembly, DNA replication and transcription. ISWI is part of the vast Snf2 family of helicase-related proteins, many of which constitute the ...
10-Dec-2011

DNA nanotechnology enables the programmed synthesis of intricate nanometer-scale structures for diverse applications in materials and biological science. Precise control over the 3D solution shape and mechanical flexibility of target designs is important to achieve desired functionality. Because experimental validation of designed nanostructures is time-consuming ...
09-Dec-2011

Previously, the OEP16.1 channel pore in the outer envelope membrane of mature pea (Pisum sativum) chloroplasts in vitro has been characterized to be selective for amino acids. Isolation of OEP16.2, a second OEP16 isoform from pea, in the current study allowed membrane localization and gene expression of OEP16 to be followed throughout seed development and ...
04-Dec-2011

Biological solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy developed rapidly in the past two decades and emerged as an important tool for structural biology. Resonance assignment is an essential prerequisite for structure determination and the characterization of motional properties of a molecule. Experiments, which rely on carbon or nitrogen detection, ...
02-Dec-2011

5-Formylcytosine (fC or 5-CHOdC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (caC or 5-COOHdC) have recently been identified as constituents of mammalian DNA. The nucleosides are formed from 5-methylcytosine (mC or 5-MedC) via 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC or 5-HOMedC) and are possible intermediates of an active DNA demethylation process. Here we show efficient syntheses of ...
01-Dec-2011
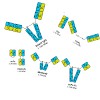
The rapid and ongoing discovery of new disease related biomarkers leads to a dramatic paradigm change in human healthcare and constitutes the basis for a truly personalized medicine. Molecular imaging enables early detection and classification of human diseases and provides valuable data for optimized, target-oriented therapies. By now, the biochemical and ...
25-Nov-2011
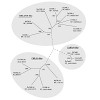
Calmodulin (CaM) is a ubiquitous sensor/ transducer of calcium signals in eukaryotic organisms. While CaM mediated calcium regulation of cytosolic processes is well established, there is growing evidence for the inclusion of organelles such as chloroplasts, mitochondria and peroxisomes into the calcium/calmodulin regulation network. A number of CaM-binding ...
20-Nov-2011
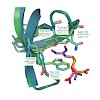
Arginine dimethylation plays critical roles in the assembly of ribonucleoprotein complexes in pre-mRNA splicing and piRNA pathways. We report solution structures of SMN and SPF30 Tudor domains bound to symmetric and asymmetric dimethylated arginine (DMA) that is inherent in the RNP complexes. An aromatic cage in the Tudor domain mediates dimethylarginine ...
18-Nov-2011
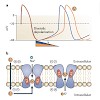
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels have a key role in the control of heart rate and neuronal excitability. Ivabradine is the first compound acting on HCN channels to be clinically approved for the treatment of angina pectoris. HCN channels may offer excellent opportunities for the development of novel anticonvulsant, anaesthetic ...
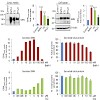
17-Nov-2011
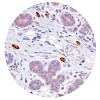
In breast cancer, a high ratio of tumour-infiltrating intraepithelial CD8+ to FoxP3+ cells is characteristic for the medullary subtype.
15-Nov-2011
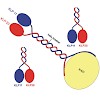
The heterotrimeric structure of kinesin-2 makes it a unique member of the kinesin superfamily; however, molecular details of the oligomer formation are largely unknown. Here we demonstrate that heterodimerization of the two distinct motor domains KLP11 and KLP20 of Caenorhabditis elegans kinesin-2 requires a dimerization seed of merely two heptads at the C ...
15-Nov-2011
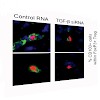
Regulatory T cells (Treg) mediate tolerance towards self-antigens by suppression of innate and adaptive immunity. In cancer patients, tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Treg suppress local anti-tumor immune responses and are often associated with poor prognosis. Markers that are selectively expressed on tumor-infiltrating Treg may serve as targets for immunotherapy of ...
15-Nov-2011
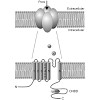
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide gated (HCN) channels pass a cationic current (Ih/If) that crucially contributes to the slow diastolic depolarization (SDD) of sinoatrial pacemaker cells and, hence, is a key determinant of cardiac automaticity and the generation of the heartbeat. However, there is growing evidence that HCN channels are not restricted ...
11-Nov-2011
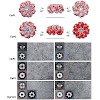
Nature provides a rich source of bioactive compounds comprising a diverse set of electrophilic core structures that are poised to react with corresponding nucleophilic residues such as serine and cysteine in enzyme active sites.These residues are usually relevant for catalysis and therefore display fine-tuned reactivity towards their dedicated substrates.We and ...
08-Nov-2011
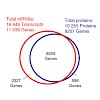
While the number and identity of proteins expressed in a single human cell type is currently unknown, this fundamental question can be addressed by advanced mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics. Online liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution MS and MS/MS yielded 166 420 peptides with unique amino-acid sequence from HeLa cells. These peptides ...
03-Nov-2011

Histone post-translational modifications play an important role in regulating chromatin structure and gene expression in vivo. Extensive studies investigated the post-translational modifications of the core histones H3 and H4 or the linker histone H1. Much less is known on the regulation of H2A and H2B modifications. Here, we show that a major modification of H2B ...
02-Nov-2011
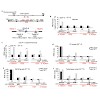
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are central to crucial cellular processes in plants and contribute to a whole range of metabolic pathways. The use of calcium ions as a secondary messenger in and around organelles is increasingly appreciated as an important mediator of plant cell signaling, enabling plants to develop or to acclimatize to changing environmental ...
01-Nov-2011
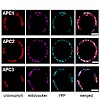
Telomerase-negative tumor cells use an alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) pathway that involves DNA recombination and repair to maintain their proliferative potential. The cytological hallmark of this process is the accumulation of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear1 protein at telomeric DNA to form ALT-associated PML bodies (APBs). Here, the de novo ...
28-Oct-2011

Direct observation of the detailed conformational fluctuations of a single protein molecule en route to its folded state has so far been realized only in silico. We have used single-molecule force spectroscopy to study the folding transitions of single calmodulin molecules. High-resolution optical tweezers assays in combination with hidden Markov analysis reveal ...
27-Oct-2011

The MOF (males absent on the first)-containing NSL (non-specific lethal) complex binds to a subset of active promoters in Drosophila melanogaster and is thought to contribute to proper gene expression. The determinants that target NSL to specific pro- moters and the circumstances in which the complex engages in regulating transcription are currently unknown. ...
24-Oct-2011
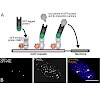
Oligonucleotides used in gene therapy and silencing are fragile compounds that degrade easily in biological environments. Porous biocompatible carrier particles may provide a useful strategy to deliver these therapeutics to their target sites. Development of appropriate delivery vehicles, however, requires a better understanding of the oligonucleotide-host ...
21-Oct-2011
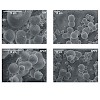
Kinases and phosphatases regulate messenger RNA synthesis through post-translational modification of the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (ref. 1). In yeast, the phosphatase Cdc14 is required for mitotic exit2,3 and for segregation of repetitive regions4. Cdc14 is also a subunit of the silencing complex RENT (refs 5,6), ...
18-Oct-2011
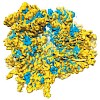
The ribosome is a highly dynamic machine responsible for protein synthesis within the cell. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and X-ray crystallography structures of ribosomal particles, alone and in complex with diverse ligands (protein factors, RNAs and small molecules), have revealed the dynamic nature of the ribosome and provided much needed insight into ...
17-Oct-2011
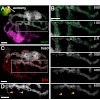
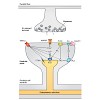
Schwann cells (SCs), the glial cells of the peripheral nervous system, cover synaptic terminals, allowing them to monitor and modulate neurotransmission. Disruption of glial coverage leads to axon degeneration and synapse loss. The cellular mechanisms that establish and maintain this coverage remain largely unknown. To address this, we labeled single SCs and ...
12-Oct-2011
Reprogramming of adult differentiated cells to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) cells has been achieved by over-expression of specific transcription factors. Nuclear reprogramming induces a series of profound changes at the telomeres of the parental differentiated cells, including a telomerase-dependent telomere elongation and the remodeling of telomeric ...
07-Oct-2011

RIG-I detects cytosolic viral dsRNA with 5′ triphosphates (5′-ppp-dsRNA), thereby initiating an antiviral innate immune response. Here we report the crystal structure of superfamily 2 (SF2) ATPase domain of RIG-I in complex with a nucleotide analogue. RIG-I SF2 comprises two RecA-like domains 1A and 2A and a helical insertion domain 2B, which together form a ...
04-Oct-2011

The genetic system contains several levels of information. Firstly, the sequence of the canonical bases A, C, G, and T/U in DNA and RNA encodes amino acids through specific base triplets. Secondly, the methylation status of the cytosine base in DNA imprints epigenetic information into the genetic system, thereby contributing to the division of genes into active ...
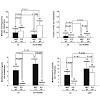
30-Sep-2011
Single particle tracking (SPT) in biological systems is a quickly growing field. Many new technologies are being developed providing new tracking capabilities, which also lead to higher demands and expectations for SPT. Following a single biomolecule as it performs its function provides quantitative mechanistic information that cannot be obtained in classical ...
30-Sep-2011
DNA methylation plays a central role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development and disease. Remarkably, the complex and changing patterns of genomic DNA methylation are established and maintained by only three DNA methyltransferases. Here we focus on DNMT1, the major and ubiquitously expressed DNA methyltransferase in vertebrates, to ...
26-Sep-2011
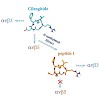
The drug Cilengitide, c(RGDf(NMe)V), is a cyclic RGD pentapeptide (R=arginine, D=aspartic acid, G=glycine) currently in clinical phase III for the treatment of brain tumors and in phase II for other cancer types.The antitumoral properties of this peptide are based on its antagonistic activity for pro-angiogenic integrins, such as alpha-v-beta-3, alpha-v-beta-5, ...
26-Sep-2011
The drug Cilengitide, c(RGDf(NMe)V), is a cyclic RGD pentapeptide (R=arginine, D=aspartic acid, G=glycine) currently in clinical phase III for the treatment of brain tumors and in phase II for other cancer types.[1] The antitumoral properties of this peptide are based on its antagonistic activity for pro-angiogenic integrins, such as alpha-v-beta3, alpha-v-beta5, ...
25-Sep-2011
Transcription of the mitochondrial genome is performed by a single-subunit RNA polymerase (mtRNAP) that is distantly related to the RNAP of bacteriophage T7, the pol I family of DNA polymerases, and single-subunit RNAPs from chloroplasts1, 2, 3, 4. Whereas T7 RNAP can initiate transcription by itself, mtRNAP requires the factors TFAM and TFB2M for binding and ...
22-Sep-2011

Cell growth is regulated during RNA polymerase (Pol) I transcription initiation by the conserved factor Rrn3/TIF- IA in yeast/humans. Here we provide a structure–function analysis of Rrn3 based on a combination of structural biology with in vivo and in vitro functional assays. The Rrn3 crystal structure reveals a unique HEAT repeat fold and a surface serine ...
22-Sep-2011

Thanks to everyone of the 360 people who attended the „Scientific Oktoberfest 2011“! We were able to experience amazing science combined with a awesome spirit. Thank you! Here you can see some impressions.
21-Sep-2011
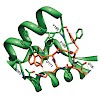
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) threaten genome stability in all kingdoms of life and are linked to cancerogenic chromosome aberrations in humans. The Mre11:Rad50 (MR) complex is an evolutionarily conserved complex of two Rad50 ATPases and a dimer of the Mre11 nuclease that senses and processes DSBs and tethers DNA for repair. ATP binding and hydrolysis by Rad50 ...
15-Sep-2011

The „Scientific Oktoberfest“ will be this years meeting point for some of the internationally most distinguished researchers in the field of Chemical Biology. The so-called „CIPSM Fest of Chemical Biology“ will be held from the 15th to the 16th of September in the Department of Chemistry of the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) München. At the two-day ...
14-Sep-2011
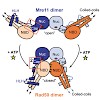
The spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria is one of the most pressing problems in human health today. In the case of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which causes lethal airway infections in cystic fibrosis and immunocompromised patients, the formation of biofilms plays an important role in antibiotic resistance and disease progression. ...
14-Sep-2011
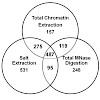
Chromatin proteins provide a scaffold for DNA packaging and a basis for epigenetic regulation and genomic maintenance. Despite understanding its functional roles, mapping the chromatin proteome (i.e. the ‘‘Chromatome’’) is still a continuing process. Here, we assess the biological specificity and proteomic extent of three distinct chromatin preparations by ...
12-Sep-2011
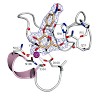
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a critical regulator of inflammation and immune surveillance, and it is specifically implicated in cancer metastasis and HIV-1 infection. On the basis of the observation that several of the known antagonists remarkably share a C2 symmetry element, we constructed symmetric dimers with excellent antagonistic activity using a ...
09-Sep-2011
Rationale: The hyperpolarization-activated current Ih that is generated by hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (HCNs) plays a key role in the control of pacemaker activity in sinoatrial node cells of the heart. By contrast, it is unclear whether Ih is also relevant for normal function of cardiac ventricles. Objective: To study the role of ...
08-Sep-2011
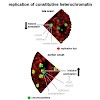
The replication of the genome is a spatio-temporally highly organized process. Yet, its flexibility throughout development suggests that this process is not genetically regulated. However, the mechanisms and chromatin modifications controlling replication timing are still unclear. We made use of the prominent structure and defined heterochromatic landscape of ...
05-Sep-2011
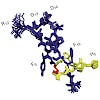
Peptides combine a high specificity for their target receptor with a low toxicity and are therefore a promising source for drug leads.However, their use has been limited because of undesirable physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. To overcome these obstacles protein scaffolds, such as ultrastable ribosomally assembled peptides, can be used together with ...
04-Sep-2011
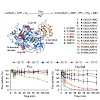
Maintenance of cellular protein homeostasis (proteostasis) depends on a complex network of molecular chaperones, proteases and other regulatory factors. Proteostasis deficiency develops during normal aging and predisposes individuals for many diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders. Here we describe sensor proteins for the comparative measurement of ...
04-Sep-2011
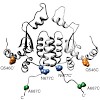
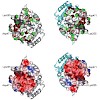
In eukaryotes, the essential dimeric molecular chaperone Hsp90 is required for the activation and maturation of specific substrates such as steroid hormone receptors, tyrosine kinases and transcription factors. Hsp90 is involved in the establishment of cancer and has become an attractive target for drug design. Here we present a structural characterization of the ...
31-Aug-2011
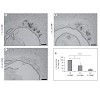
Neurons of the Grueneberg ganglion (GG) in the anterior na- sal region of mouse pups respond to cool temperatures and to a small set of odorants. While the thermosensory reactiv- ity appears to be mediated by elements of a cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) cascade, the molecular mecha- nisms underlying the odor-induced responses are unclear. Since ...
29-Aug-2011

Single cortical neurons in the mammalian brain receive signals arising from multiple sensory input channels. Dendritic integration of these afferent signals is critical in determining the amplitude and time course of the neurons’ output signals. As of yet, little is known about the spatial and temporal organization of converging sensory inputs. Here, we combined ...
28-Aug-2011
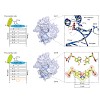
The universal genetic code relies on two hydrogen-bonded Watson–Crick base pairs that can form 64 triplet codons. This places a limit on the number of amino acids that can be encoded, which has motivated efforts to create synthetic base pairs that are orthogonal to the natural ones. An additional base pair would result in another 61 triplet codons. Artificial ...
23-Aug-2011
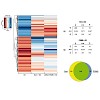
The estrogen receptor-alpha (ERa) determines the phenotype of breast cancers where it serves as a positive prognostic indicator. ERa is a well-established target for breast cancer therapy, but strategies to target its function remain of interest to address therapeutic resistance and further improve treatment. Recent findings indicate that proteasome inhibition ...
18-Aug-2011
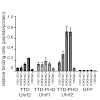
Gene expression is regulated by DNA as well as histone modifications but the crosstalk and mechanistic link between these epigenetic signals are still poorly understood. Here we investigate the multi-domain protein Uhrf2 that is similar to Uhrf1, an essential cofactor of maintenance DNA methylation. Binding assays demonstrate a cooperative interplay of Uhrf2 ...
11-Aug-2011
Previous studies of the ferret visual cortex indicate that the development of direction selectivity requires visual experience. Here,weused two-photon calcium imaging to study the development of direction selectivity in layer 2/3 neurons of the mouse visual cortex in vivo. Surprisingly, just after eye opening nearly all orientation-selective neurons were also ...
08-Aug-2011
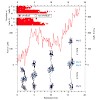
The highly oriented filamentous protein network of muscle constantly experiences significant mechanical load during muscle operation. The dimeric protein myomesin has been identified as an important M-band component supporting the mechanical integrity of the entire sarcomere. Recent structural studies have revealed a long αlpha-helical linker between the ...
06-Aug-2011
AlphavBeta3 and AlphavBeta5 integrins are attractive target structures for cancer therapy as they are upregulated in tumor 27 and tumor associated host cells and play a pivotal role for tumor growth and metastasis. Gene vectors such as 28 polyplex micelles consisting of thiolated PEG-block-poly(lysine) copolymers complexed with plasmid DNA 29 can be targeted to ...
03-Aug-2011
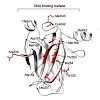
The function of nuclear actin is poorly understood. It is known to be a discrete component of several chromatin-modifying complexes. Nevertheless, filamentous forms of actin are important for various nuclear processes as well. Nuclear actin is often associated with nuclear actin-related protein Arp4 and other actin-related proteins like Arp8 in the INO80 ...
03-Aug-2011
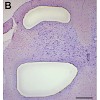
A large body of evidence indicates that nitric oxide (NO) and cGMP contribute to central sensitization of pain pathways during inflammatory pain. Here, we investigated the distribution of cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels in the spinal cord, and identified the CNG channel subunit CNGA3 as a putative cGMP target in nociceptive processing. In situ ...
02-Aug-2011
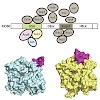
Structural studies of multi-protein complexes, whether by X-ray diffraction, scattering, NMR spectroscopy or electron microscopy, require stringent quality control of the component samples. The inability to produce ‘keystone’ subunits in a soluble and correctly folded form is a serious impediment to the reconstitution of the complexes. Co-expression of the ...
28-Jul-2011
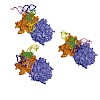
Telethonin (also known as titin-cap or t-cap) is a 19-kDa Z-disk protein with a unique beta-sheet structure, hypothesized to assemble in a palindromic way with the N-terminal portion of titin and to constitute a signalosome participating in the process of cardiomechanosensing. In addition, a variety of telethonin mutations are associated with the development of ...
28-Jul-2011

In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), transit peptides for chloroplast-destined preproteins can be phosphorylated by the protein kinases STY8, STY17, and STY46. In this study, we have investigated the in vitro properties of these plant-specific kinases. Characterization of the mechanistic functioning of STY8 led to the identification of an essential threonine in ...
25-Jul-2011

Cellular development requires the silencing and activation of specific gene sequences in a well-orchestrated fashion. Transcriptional gene silencing is associated with the clustered methylation of cytosine bases (C) in CpG units of promoters. The methylation occurs at position C5 of cytosine to give 5- methylcytosine (mC) with the help of special DNA ...
24-Jul-2011
Several lines of recent evidence support a role for chromatin in splicing regulation. Here, we show that splicing can also contribute to histone modification, which implies bidirectional communication between epigenetic mechanisms and RNA processing. Genome-wide analysis of histone methylation in human cell lines and mouse primary T cells reveals that ...
22-Jul-2011

Vertebrate embryos are derived from a transitory pool of pluripotent cells. By the process of embryonic induction, these precursor cells are assigned to specific fates and differentiation programs. Histone post-translational modifications are thought to play a key role in the establishment and maintenance of stable gene expression patterns underlying these ...
22-Jul-2011
TFIIE and the archaeal homolog TFE enhance DNA strand separation of eukaryotic RNAPII and the archaeal RNAP during transcription initiation by an unknown mechanism. We have developed a fluorescently labeled recombinant M. jannaschii RNAP system to probe the archaeal transcription initiation complex, consisting of promoter DNA, TBP, TFB, TFE, and RNAP. We have ...
21-Jul-2011
The wogonin-containing herb Scutellaria baicalensis has successfully been used for curing various diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. Wogonin has been shown to induce apoptosis in different cancer cells and to suppress growth of human cancer xenografts in vivo. However, its direct targets remain unknown. In this study, we demonstrate for the first time that ...
21-Jul-2011
Initiation of X-chromosome inactivation in female mammals depends on the non-coding RNA Xist. We have solved the NMR structure of a 14-nucleotide hairpin with a novel AUCG tetraloop fold from a Xist A-repeat that is essential for silencing. The 1H, 13C, 15N and 31P chemical shift assignments are reported.
20-Jul-2011
Nowadays, personalized medicine is considered to be of utmost importance to target the different causes of identical phenotypes. For example, cancer of the same type can significantly differ in its biochemical phenotypes and thus its molecular profile between patients. The disease-specific characterization of malignant cells at the molecular level is a ...
18-Jul-2011
Bacteria communicate by sending and receiving chemical cues in a process termed ‘quorum sensing’. New research shows how five feedback loops of the Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing cascade ensure signal integration and transmission fidelity, with one loop controlling signal sensitivity by regulating receptor ratios.
17-Jul-2011
Recent work has shown that RNA polymerase (Pol) II can be recruited to and transcribe distal regulatory regions. Here we analyzed transcription initiation and elongation through genome-wide localization of Pol II, general transcription factors (GTFs) and active chromatin in developing T cells. We show that Pol II and GTFs are recruited to known T cell–specific ...
15-Jul-2011

The generation of metameric body plans is a key process in development. In Drosophila segmentation, periodicity is established rapidly through the complex transcriptional regulation of the pair-rule genes. The ‘primary’ pair-rule genes generate their 7-stripe expression through stripe-specific cis-regulatory elements controlled by the preceding non-periodic ...
13-Jul-2011
Many cellular functions involve multi-domain proteins, which are composed of structurally independent modules connected by flexible linkers. Although it is often well understood how a given domain recognizes a cognate oligonucleotide or peptide motif, the dynamic interaction of multiple domains in the recognition of these ligands remains to be characterized. Here ...
11-Jul-2011

Active chromatin remodelling is integral to the DNA damage response in eukaryotes, as damage sensors, signalling molecules and repair enzymes gain access to lesions. A variety of nucleosome remodel- ling complexes is known to promote different stages of DNA repair. The nucleosome sliding factors CHRAC/ACF of Drosophila are involved in chromatin organization ...
11-Jul-2011
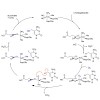
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC) was recently discovered as a new constituent of mammalian DNA. Besides 5-methylcytosine (mC), it is the only other modified base in higher organisms. The discovery is of enormous importance because it shows that the methylation of cytosines to imprint epigenetic information is not a final chemical step that leads to gene silencing ...
07-Jul-2011
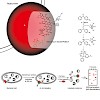
Vancomycin is a potent glycopeptide antibiotic that has evolved to specifically bind to the D-Ala-D-Ala dipeptide termini of nascent peptidoglycans. Although this mode of action is well established, several studies indicate that vancomycin and analogues exploit noncanonical target sites. In order to address all vancomycin targets in clinically relevant ...
06-Jul-2011
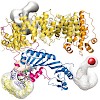
Swi2/Snf2-typeATPases regulate genome-associated processes such as transcription, replication and repair by catalysing the disruption, assembly or remodelling of nucleosomes or other protein–DNA complexes1,2. It has been suggested that ATP-driven motor activity along DNA disrupts target protein–DNA interactions in the remodelling reaction3–5. However, the complex ...
Evaluation of α-Pyrones and Pyrimidones as Photoaffinity Probes for Affinity-Based Protein Profiling
05-Jul-2011
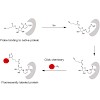
α-Pyrones and pyrimidones are common structural motifs in natural products and bioactive compounds. They also display photochemistry that generates high-energy intermediates that may be capable of protein reactivity. A library of pyrones and pyrimidones was synthesized, and their potential to act as photoaffinity probes for nondirected affinity-based protein ...
26-Jun-2011
The individual functional properties and spatial arrangement of afferent synaptic inputs on dendrites have a critical role in the processing of information by neurons in the mammalian brain. Although recent work has identified visually-evoked local dendritic calcium signals in the rodent visual cortex, sensory-evoked signalling on the level of dendritic spines, ...
22-Jun-2011
Recent discovery of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) in genomic DNA raises the question how this sixth base is recognized by cellular proteins. In contrast to the methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) of MeCP2, we found that the SRA domain of Uhrf1, an essential factor in DNA maintenance methylation, binds 5hmC and 5-methylcytosine containing substrates with similar ...
22-Jun-2011

Topical application of small molecule Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) agonists is highly effective for the treatment of skin tumors, whereas their systemic application has been largely unsuccessful for cancer therapy. One reason may be that repeated systemic application of TLR ligands can induce a state of immune unresponsiveness, termed TLR tolerance. We show here ...
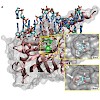
21-Jun-2011
Due to their endosymbiotic origin, chloroplasts are completely reliant on post-translational import of their resident proteins.1 Integral membrane proteins comprise approximately 20 % of the total estimated chloroplast proteome.2, 3 Based on several proteomic analyses, 20 % of all membrane proteins are located in the inner envelope (IE).4–6 Judging from the ...
19-Jun-2011
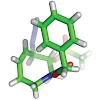
Loline is a small alkaloid that, in spite of its simple-looking structure, has posed surprising challenges to synthetic chemists. It has been known for more than a century and has been the subject of extensive biological investigations, but only two total syntheses have been achieved to date. Here, we report an asymmetric total synthesis of loline that, with less ...
09-Jun-2011

Photochromic channel blockers provide a conceptually simple and convenient way to modulate neuronal activity with light. We have recently described a family of azobenzenes that function as tonic blockers of Kv channels but require UV-A light to unblock and need to be actively switched by toggling between two different wavelengths. We now introduce red-shifted ...
09-Jun-2011
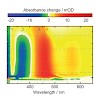
The photophysics of 1-methyl-2(1H)-pyrimidinone (1MP) dissolved in water is investigated by steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence, UV/Vis absorption, and IR spectroscopy. In the experiments, excitation light is tuned to the lowest-energy absorption band of 1MP peaking at 302 nm. At room temperature (291 K) its fluorescence lifetime amounts to 450 ps. With ...
07-Jun-2011
Highly sensitive fluorescence microscopy techniques allow single nanoparticles to be tracked during their uptake into living cells with high temporal and spatial resolution. From analysis of the trajectories, random motion can be discriminated from active transport and the average transport velocity and/or diffusion coefficient determined. Such an analysis ...
05-Jun-2011

The correlation of light and electron microscopy of complex tissues remains a major challenge. Here we report near-infrared branding (NIRB), which facilitates such correlation by using a pulsed, near-infrared laser to create defined fiducial marks in three dimensions in fixed tissue. As these marks are fluorescent and can be photo-oxidized to generate electron ...
02-Jun-2011
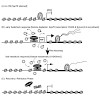
Gene expression is highly dynamic and many genes show a wide range in expression over several orders of magnitude. This regulation is often mediated by sequence specific transcription factors. In addition, the tight packaging of DNA into chromatin can provide an additional layer of control resulting in a dynamic range of gene expression covering several orders of ...
31-May-2011
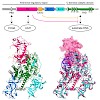
DNA methylation, the postreplicative transfer of a methyl group to the C5 position of cytosine bases, was the first epigenetic modification identified and has been intensively studied for more than half a century. By now it is clear that Dnmt1, the major eukaryotic DNA methyltransferase, faithfully maintains genome-wide methylation patterns and plays an essential ...
27-May-2011
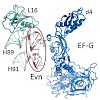
The ribosome is a major target in the bacterial cell for antibiotics. Here, we dissect the effects that the thiopeptide antibiotics thiostrepton (ThS) and micrococcin (MiC) as well as the orthosomycin antibiotic evernimicin (Evn) have on translational GTPases. We demonstrate that, like ThS, MiC is a translocation inhibitor, and that the activation by MiC of the ...
27-May-2011
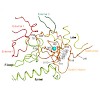
During gene transcription, the RNA polymerase (Pol) active center can catalyze RNA cleavage. This intrinsic cleavage activity is strong for Pol I and Pol III but very weak for Pol II. The reason for this difference is unclear because the active centers of the polymerases are virtually identical. Here we show that Pol II gains strong cleavage activity when the ...
18-May-2011
Most chloroplast and mitochondrial proteins are synthesized in the cytosol of the plant cell and have to be imported into the organelles post-translationally. Molecular chaperones play an important role in preventing protein aggregation of freshly translated preproteins and assist in maintaining the preproteins in an import competent state. Preproteins can ...
17-May-2011

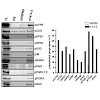
There are only few reports on protein products originating from overlapping mammalian genes even though computational predictions suggest that an appreciable fraction of mammalian genes could potentially overlap. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics has now acquired the tools to probe proteins in an unbiased manner, providing direct evidence of the output of the ...
12-May-2011
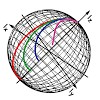
We present a novel concept for rf pulses and optimal control designed cross-polarization experiments for quadrupolar nuclei. The methods are demonstrated for 2H CP-MAS and 2H multiple-pulse NMR of perdeuterated proteins, for which sensitivity enhancements up to an order of magnitude are presented relative to commonly used approaches. The so-called RESPIRATION rf ...
04-May-2011
The barrel-shaped serine protease ClpP degrades misfolded, damaged, and regulatory proteins. Substrate proteins enter the ClpP barrel through the two axial pores, but it is unclear how the peptide products exit the barrel. Here we report the structure of ClpP from Staphylococcus aureus, which reveals a previously unobserved compressed state of the barrel. A ...
02-May-2011

Structural characterization of insoluble proteins often relies on solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Perdeuteration and partial back-substitution of exchangeable protons, as proposed for crystalline model proteins, is now shown to lead to beneficial proton spectra for heterogeneous systems, such as fibrils formed by the Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid peptide Aβ40, the ...
01-May-2011
A major problem for chloroplast research remains that plant species which are utilized in order to obtain a high amount of isolated intact chloroplasts are not sequenced on a genomic base. Thus it is difficult to combine the data from biochemical experiments with genomic data and employ techniques such as MS to identify low abundant proteins. There are plant ...
28-Apr-2011
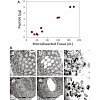
Proteomic analysis of samples isolated by laser capture microdissection from clinical specimens requires sample preparation and fractionation methods suitable for small amounts of protein. Here we describe a streamlined filter-aided sample preparation (FASP) workflow that allows efficient analysis of lysates from low numbers of cells. Addition of carrier ...
24-Apr-2011

The interleukin-4-inducing principle from Schistosoma mansoni eggs (IPSE/alpha-1) is a major immunogenic component of schistosomes. It potently triggers the release of interleukin-4 from basophilic granulocytes in an IgE-dependent manner, suggesting a key function in the modulation of the host’s immune response to Schistosoma mansoni infection. Here we present ...
22-Apr-2011
RNA polymerase (Pol) II transcribes protein-coding genes in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and consists of 12 polypeptide subunits. It is unknown how Pol II is imported into the nucleus. Here we show that Pol II nuclear import requires the protein Iwr1 and provide evidence for cyclic Iwr1 function. Iwr1 binds Pol II in the active center cleft between the two ...
20-Apr-2011

The DFG will fund the program of emphasis on inidividuality of bacteria which is coordinated by CIPSM's Kirsten Jung. In this program scientists from a range of disciplines are trying to show whether or not bacteria of a population which are genetically identical and have the same phenotype show the same properties and behave in the same manner or not. The DFG ...
Total Chemical Synthesis of an Integral Membrane Enzyme: Diacylglycerol Kinase from Escherichia coli
18-Apr-2011
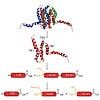
Recent progress in chemical protein synthesis has provided access to many small to medium-sized proteins. However, the highly important class of membrane proteins comprising multimembrane-spanning receptors and ion channels as well as integral membrane enzymes remains elusive with regard to chemical synthesis. Only certain moderately sized membrane proteins have ...
17-Apr-2011

The ubiquitous SecY–Sec61 1 complex translocates nascent secretory proteins across cellular membranes and integrates membrane proteins into lipid bilayers. Several structures of mostly detergent-solubilized Sec complexes have been reported. Here we present a single-particle cryo-EM structure of the SecYEG complex in a membrane environment, bound to a translating ...
17-Apr-2011
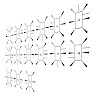
Recent progress in peptide synthesis simplified the synthesis of multiple N-methylation of peptides. To evaluate how multiple N-methylation affects the bioavailability of peptides, a poly alanine cyclic hexapeptide library (n = 54), varying in the number of N-methyl (N-Me) groups (1−5 groups) and their position, was synthesized. The peptides were evaluated for ...
15-Apr-2011

Mediator is a multiprotein co-activator of RNA poly- merase (Pol) II transcription. Mediator contains a conserved core that comprises the ‘head’ and ‘middle’ modules. We present here a structure– function analysis of the essential Med11/22 hetero- dimer, a part of the head module. Med11/22 forms a conserved four-helix bundle domain with C-terminal extensions, ...
15-Apr-2011

Nuclear actin and actin-related proteins (Arps) are integral components of various chromatin-remodelling complexes. Actin in such nuclear assemblies does not form filaments but associates in defined complexes, for instance with Arp4 and Arp8 in the INO80 remodeller. To understand the relationship between nuclear actin and its associated Arps and to test the ...
13-Apr-2011
The molecular chaperone Hsp90 regulates the activity and stability of a set of client proteins. Despite prog- ress in understanding its mechanism, the interaction of Hsp90 with clients has remained enigmatic. Now, in a recent issue of Molecular Cell, Street and coworkers present results that integrate the client in the Hsp90 chaperone cycle.
12-Apr-2011
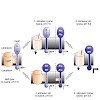
Background: In an acidic and lysine-rich environment Escherichia coli induces expression of the cadBA operon which encodes CadA, the lysine decarboxylase, and CadB, the lysine/cadaverine antiporter. cadBA expression is dependent on CadC, a membrane-integrated transcriptional activator which belongs to the ToxR-like protein family. Activation of CadC requires two ...
12-Apr-2011
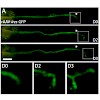
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), damaged axons regenerate successfully, whereas axons in the CNS fail to regrow. In neurons of the dorsal root ganglia (DRG), which extend branches to both the PNS and CNS, only a PNS lesion but not a CNS lesion induces axonal growth. How this differential growth response is regulated in vivo is only incompletely understood. ...
05-Apr-2011
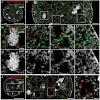
We studied the nuclear topography of RNA transcription and DNA replication in mammalian cell types with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy, which offers a resolution beyond the classical Abbe/Raleigh limit. Three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM) demonstrated a network of channels and wider lacunas, called the interchromatin ...
04-Apr-2011
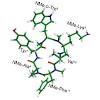
A focused multiply N-methylated library of a cyclic hexapeptidic somatostatin analogue: MK678 cyclo(−MeAYwKVF−) was generated, which resulted in the unexpected observation of an efficacious tetra-N-methylated analogue, cyclo(−MeAYMewMeKVMeF−) with a potent inhibitory action on sensory neuropeptide release in vitro and on acute neurogenic inflammatory response in ...
01-Apr-2011

The carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) in mammals undergoes extensive posttranslational modification, which is essential for transcriptional initiation and elongation. Here, we show that the CTD of RNAPII is methylated at a single arginine (R1810) by the coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1). Although methylation at ...
01-Apr-2011

The MR (Mre11 nuclease and Rad50 ABC ATPase) complex is an evolutionarily conserved sensor for DNA double-strand breaks, highly genotoxic lesions linked to cancer development.MRcan recognize and process DNA ends even if they are blocked and misfolded. To reveal its mechanism, we determined the crystal structure of the catalytic head of Thermotoga maritima MR and ...
01-Apr-2011
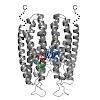
In eukaryotes, hundreds of mRNAs are localized by specialized transport complexes. For localization, transcripts are recognized by RNA-binding proteins and incorporated into motor-containing messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs). To date, the molecular assembly of such mRNPs is not well understood and most details on cargo specificity remain unresolved. ...
31-Mar-2011
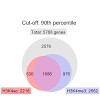
Methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me) is an evolutionarily conserved modification whose role in the regulation of gene expression has been extensively studied. In contrast, the function of H3K4 acetylation (H3K4ac) has received little attention because of a lack of tools to separate its function from that of H3K4me. Here we show that, in addition to being ...
29-Mar-2011

Much progress has been made concerning histone function in the nucleus; however, following their synthesis, how their marking andsubcellular trafficking are regulated remains tobeexplored.To gainaninsight into these issues, wefocusedonsoluble histonesand analyzed endogenous and tagged H3 histones in parallel. We distinguished six complexes that we could place to ...
A reversible form of axon damage in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis
27-Mar-2011
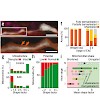
In multiple sclerosis, a common inflammatory disease of the central nervous system, immune-mediated axon damage is responsible for permanent neurological deficits1,2. How axon damage is initiated is not known. Here we use in vivo imaging to identify a previously undescribed variant of axon damage in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. This process, termed ‘focal ...
26-Mar-2011

The modification of serine and threonine residues in proteins by a single N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) residue is an emerging post-translational modification (PTM) with broad biological implications. However, the systematic or large-scale analysis of this PTM is hampered by several factors, including low stoichiometry and the lability of the O-glycosidic bond ...
25-Mar-2011
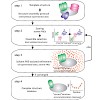
Understanding the function of biomolecular complexes requires their structural analysis at atomic resolution. To solve high-resolution structures by ab initio calculations typically data from NMR spectroscopy or X-ray crystallography are employed. In the latter approach, intrinsic flexibility and dynamics may prevent crystallization or introduce artificial ...
24-Mar-2011

Magic-angle spinning (MAS) solid-state NMR becomes an increasingly important tool for the determination of structures of membrane proteins and amyloid fibrils. Extensive deuteration of the protein allows multidimensional experiments with exceptionally high sensitivity and resolution to be obtained. Here we present an experimental strategy to measure highly ...
22-Mar-2011
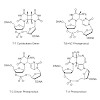
UV irradiation of cellular DNA leads to the formation of a number of defined mutagenic DNA lesions. Here we report the discovery of new intrastrand C(4−8)G and G(8−4)C cross-link lesions in which the C(4) amino group of the cytosine base is covalently linked to the C(8) position of an adjacent dG base. The structure of the novel lesions was clarified by ...
21-Mar-2011
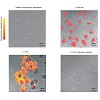
Mesoporous silica nanomaterials are a novel class of materials that offer a highly complex porous network with nanometre-sized channels into which a wide amount of differently sized guests can be incorporated. This makes them an ideal host for various applications for example in catalysis, chromatography and nanomedicine. For these applications, analyzing the ...
18-Mar-2011
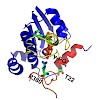
The metabolic processes of a cell comprise a network of interrelated molecular pathways. Control and regulation of these pathways under variable environmental conditions is vital and takes place at the transcriptional, translational, and posttranslational level. The eukaryotic molecular chaperone and heat-shock protein Hsp90, which is involved in the specific ...
18-Mar-2011

Take a look at the new Cell movie clip of CIPSM's Karl-Peter Hopfner and group called "Sensing DMA Damage". Click here to watch "Sensing DMA Damage" on YouTube
16-Mar-2011
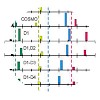
6,7-Dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine serves as fluorophore in lumazine proteins (LumP) of luminescent bacteria. The molecule exhibits several characteristic vibrational absorption bands between 1300 and 1750 cm-1 in its electronic ground state. The IR-absorption pattern of the singlet excited ππ* state was monitored via ultrafast infrared spectroscopy after ...
15-Mar-2011
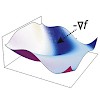
Structural analysis of multi-domain protein complexes is a key challenge in current biology and a prerequisite for understanding the molecular basis of essential cellular processes. The use of solution techniques is important for characterizing the quaternary arrangements and dynamics of domains and subunits of these complexes. In this respect solution NMR is the ...
14-Mar-2011
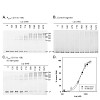
Expression of lysP, which encodes the lysine-specific transporter LysP in Escherichia coli, is regulated by the concentration of exogenous available lysine. In this study, the LysR-type transcriptional regulator ArgP was identified as the activator of lysP expression. At lysine concentrations higher than 25 µM, lysP expression was shut off and phenocopied an argP ...
12-Mar-2011
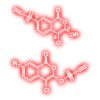
Activity-based probes (ABPs) have found increasing use in functional proteomics studies. Recently, ABPs that can be employed in combination with click chemistry gained particular attention due to their flexible application in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, there is a continuous need for new ABPs that target small subsets of enzymes. We here report novel clickable ...
11-Mar-2011
Post-translational poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation has diverse essential functions in the cellular response to DNA damage as it contributes to avid DNA damage detection and assembly of the cellular repair machinery but extensive modification eventually also induces cell death. While there are 17 human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) genes, there is only one ...
10-Mar-2011
HIV (human immunode_ciency virus) diverts the cellular ESCRT (endosomal sorting complex required for transport) machinery to promote virion release from infected cells. The ESCRT consists of four heteromeric complexes (ESCRT-0 to ESCRT-III), which mediate different membrane abscission processes, most importantly formation of intralumenal vesicles at ...
10-Mar-2011
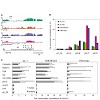
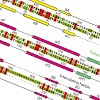
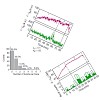
The ubiquitous tandem kinase JIL-1 is essential for Drosophila development. Its role in defining decondensed domains of larval polytene chromosomes is well established, but its involvement in transcription regulation has remained controversial. For a first comprehensive molecular characterisation of JIL-1, we generated a high-resolution, chromosome-wide ...
09-Mar-2011
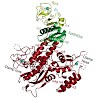
Related RNA polymerases (RNAPs) carry out cellular gene transcription in all three kingdoms of life. The universal conservation of the transcription machinery extends to a single RNAP-associated factor, Spt5 (or NusG in bacteria), which renders RNAP processive and may have arisen early to permit evolution of long genes. Spt5 associates with Spt4 to form the ...
08-Mar-2011
06-Mar-2011
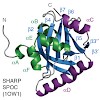
Eukaryotic transcription is regulated by interactions between gene-specific activators and the coactivator complex Mediator. Here we report the NMR structure of the Mediator subunit Med25 (also called Arc92) activator interaction domain (ACID) and analyze the structural and functional interaction of ACID with the archetypical acidic transcription activator VP16. ...
04-Mar-2011
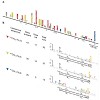
In mammalian genomes a sixth base, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC), is generated by enzymatic oxidation of 5-methylcytosine (mC). This discovery has raised fundamental questions about the functional relevance of hmC in mammalian genomes. Due to their very similar chemical structure, discrimination of the rare hmC against the far more abundant mC is technically ...
03-Mar-2011
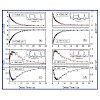
Femtosecond IR-pump-IR-probe experiments with independently tunable pulses are used to monitor the ultrafast response of selected IR absorption bands to vibrational excitation of other modes of Fmoc-nitrophenylalanine. The absorptions of both NO2-bands change rapidly within <2 ps upon excitation of other vibrational modes. The results point to considerable ...
03-Mar-2011
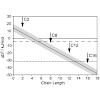
The fusion of biological membranes is mediated by integral membrane proteins with Alpha-helical transmembrane segments. Additionally, those proteins are often modified by the covalent attachment of hydrocarbon chains. Previously, a series of de novo designed Alpha-helical peptides with mixed Leu/Val sequences was presented, mimicking fusiogenically active ...
01-Mar-2011
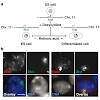
In mammals, dosage compensation between male and female cells is achieved by inactivating one female X chromosome (Xi). Late replication of Xi was proposed to be involved in the maintenance of its silenced state. Here, we show a highly synchronous replication of the Xi within 1 to 2 h during early-mid S-phase by following DNA replication in living mammalian cells ...
25-Feb-2011
Sequential processing of the beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) by beta- and gamma - secretase generates the amyloid beta - peptide (Abeta), which is widely believed to play a causative role in Alzheimer´s disease (AD). Selective lowering of the pathogenic 42 amino acid variant of Abeta by gamma-secretase modulators (GSMs) is a promising therapeutic strategy. ...
25-Feb-2011
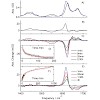
Self-assembly and aggregation of proteins or peptides into amyloid fibrils have attracted wide attention due to their high relevance for a variety of amyloid-related diseases.[1–3] Furthermore, amyloids show interesting material properties which make them ideal candidates for the production of nanostructures and molecular nanobiomaterials, where building blocks ...
25-Feb-2011

Molecular self-assembly with scaffolded DNA origami enables building custom-shaped nanometer-scale objects with molecular weights in the megadalton regime. Here we provide a practical guide for design and assembly of scaffolded DNA origami objects. We also introduce a computational tool for predicting the structure of DNA origami objects and provide information ...
23-Feb-2011

During gene transcription, RNA polymerase (Pol) II moves forwards along DNA and synthesizes messenger RNA. However, at certain DNA sequences, Pol II moves backwards, and such backtracking can arrest transcription. Arrested Pol II is reactivated by transcription factor IIS (TFIIS), which inducesRNAcleavage that is required for cell viability1. Pol II arrest and ...
22-Feb-2011
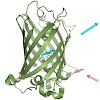
A novel kind of fluorescent protein relying on the intramolecular interplay between two different fluorophores, one of chemical origin and one of biological origin, was developed. The fluorescent non-natural amino acid L-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl)ethylglycine was site-specifically incorporated into the recombinant enhanced cyan fluorescent protein (eCFP) at a ...
16-Feb-2011
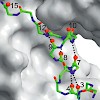
Understanding the mechanism of protein folding requires a detailed knowledge of the structural properties of the barriers separating unfolded from native conformations. The S-peptide from ribonuclease S forms its Alpha-helical structure only upon binding to the folded S-protein. We characterized the transition state for this binding-induced folding reaction at ...
16-Feb-2011
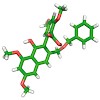
A potentially biomimetic approach toward the complex polyketide A-74528 is described. It is based on highly substituted biaryl compounds, synthesized using advanced cross-coupling and condensation methodologies.
14-Feb-2011
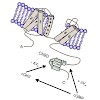
Opening of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels is facilitated by direct binding of cyclic nucleotides to a cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (CNBD) in the C-terminus. Here, we show for the first time that in the HCN2 channel cGMP can also exert an inhibitory effect on gating via cGMP-dependent protein kinase II (cGKII)-mediated ...
11-Feb-2011
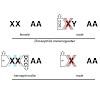
Dosage compensation processes in flies and worms provide a unique opportunity to study common regulatory principles of thousands of genes.Technological advancement in the recent years has allowed for the comprehensive description of key aspects such as the targeting of the regulatory factors,the emerging chromatin structure changes and the ensuing subtle ...
11-Feb-2011
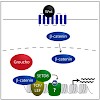
Growth factor signaling pathways regulate a broad spectrum of cellular processes ranging from proliferation to differentiation and tissue homeostasis. Activation of a signaling pathway ultimately leads to transcriptional changes in specific target genes. Although the molecular identities of many signaling pathway components have been revealed over the last years, ...
11-Feb-2011
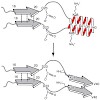
The structures of oligomeric intermediate states in the aggregation process of Alzheimer’s disease b-amyloid peptides have been the subject of debate for many years. Bacterial inclusion bodies contain large amounts of small heat shock proteins (sHSPs), which are highly homologous to those found in the plaques of the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. sHSPs ...
10-Feb-2011
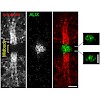
Following partitioning of cytoplasmic contents by cleavage furrow ingression, animal cells remain connected by an intercellular bridge, which subsequently splits by abscission. Here, we examined intermediate stages of abscission in human cells, using live imaging, three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy, and electron tomography. We identified helices ...
10-Feb-2011

As the nascent polypeptide chain is being synthesized, it passes through a tunnel within the large ribosomal subunit and emerges at the solvent side where protein folding occurs. Despite the universality and conservation of dimensions of the ribosomal tunnel, a functional role for the ribosomal tunnel is only beginning to emerge: Rather than a passive conduit for ...
07-Feb-2011
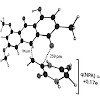
Speculations on the biosynthetic origin of natural products continue to inspire synthetic chemists and have led to many elegant and efficient total syntheses. Many of these involve cascade reactions, where a high-energy substrate is formed and then spontaneously reacts further to create increasingly more complex products. As such, biomimetic strategies do not ...
04-Feb-2011
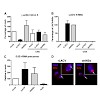
La Crosse encephalitis virus (LACV) is a mosquito-borne member of the negative-strand RNA virus family Bunyaviridae. We have previously shown that the virulence factor NSs of LACV is an efficient inhibitor of the antiviral type I interferon system. A recombinant virus unable to express NSs (rLACVdelNSs) strongly induced interferon transcription, whereas the ...
04-Feb-2011
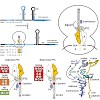
In this issue of Molecular Cell, Ramu et al. demonstrate that nascent peptides located within the ribosomal tunnel can talk back to the peptidyl transferase center to induce translational stalling by restricting the species of aminoacyl-tRNAs that can bind there.
02-Feb-2011
Numerous loss-of-function mutations in the progranulin (GRN) gene cause frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin and TAR–DNAbinding protein 43-positive inclusions by reduced production and secretion of GRN. Consistent with the observation thatGRN has neurotrophic properties, pharmacological stimulation ofGRNproduction is a promising approach to rescue ...
02-Feb-2011
Several mammalian proteins involved in chromatin and DNA modification contain CXXC zinc finger domains. We compared the structure and function of the CXXC domains in the DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1 and the methylcytosine dioxygenase Tet1. Sequence alignment showed that both CXXC domains have a very similar framework but differ in the central tip region. Based on ...
26-Jan-2011
Metabotropic glutamate receptors type 1 (mGluR1s) are required for a normal function of the mammalian brain. They are particularly important for synaptic signaling and plasticity in the cerebellum. Unlike ionotropic glutamate receptors that mediate rapid synaptic transmission, mGluR1s produce in cerebellar Purkinje cells a complex postsynaptic response consisting ...
25-Jan-2011

In mammals Dnmt1 is the DNA methyltransferase chiefly responsible for maintaining genomic methylation patterns through DNA replication cycles, but how its maintenance activity is controlled is still not well understood. Interestingly, Uhrf1, a crucial cofactor for maintenance of DNA methylation by Dnmt1, is endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Here, we show ...
24-Jan-2011

Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) supports proinsulin folding as chaperone and isomerase. Here, we focus on how the two PDI functions influence individual steps in the complex folding process of proinsulin. We generated a PDI mutant (PDI‐aba′c) where the b′ domain was partially deleted, thus abolishing peptide binding but maintaining a PDI‐like redox potential. ...
24-Jan-2011
The membrane-integral transcriptional activator CadC comprises sensory and transcriptional regulatory functions within one polypeptide chain. Its C-terminal periplasmic domain, CadCpd, is responsible for sensing of environmental pH as well as for binding of the feedback inhibitor cadaverine. Here we describe the crystal structure of CadCpd (residues 188–512) ...
20-Jan-2011
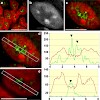
We used chicken retinospheroids (RS) to study the nuclear architecture of vertebrate cells in a three-dimensional (3D) cell culture system. The results showed that the different neuronal cell types of RS displayed an extreme form of radial nuclear organization. Chromatin was arranged into distinct radial zones which became already visible after DAPI staining. The ...
19-Jan-2011

Human epithelia are permanently challenged by bacteria and fungi, including commensal and pathogenic microbiota. In the gut, the fraction of strict anaerobes increases from proximal to distal, reaching 99% of bacterial species in the colon. At colonic mucosa, oxygen partial pressure is below 25% of airborne oxygen content, moreover microbial metabolism causes ...
19-Jan-2011
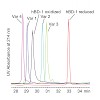
Human epithelia are permanently challenged by bacteria and fungi, including commensal and pathogenic microbiota. In the gut, the fraction of strict anaerobes increases from proximal to distal, reaching 99% of bacterial species in the colon. At colonic mucosa, oxygen partial pressure is below 25% of airborne oxygen content, moreover microbial metabolism causes ...
18-Jan-2011

As nascent polypeptide chains are synthesized, they pass through a tunnel in the large ribosomal subunit. Interaction between specific nascent chains and the ribosomal tunnel is used to induce translational stalling for the regulation of gene expression. One well-characterized example is the Escherichia coli SecM (secretion monitor) gene product, which induces ...
17-Jan-2011
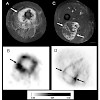
PET imaging of integrin alpha-v-beta-3 expression has been studied intensely by the academia and recently also by the industry. Imaging of integrin alpha-v-beta-3 expression is of great potential value, as the integrin alpha-v-beta-3 is a key player in tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. Therefore PET imaging of this target might be a suitable in-vivo biomarker of ...
13-Jan-2011
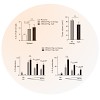
Purpose: The Toll-like receptor (TLR) 9 ligand CpG has been used successfully for the immunotherapy of cancer. Chronic CpG application in tumor-free hosts leads, however, to the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), which can cause T-cell suppression and may thus hamper the development of an effective immune response. Here, we investigated the ...
10-Jan-2011
The proteasome's participation in essential biological processes such as stress response, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and antigen presentation has been well established.[1] It is, therefore, not surprising that academia and the pharmaceutical industry have made efforts to develop a range of small synthetic inhibitors against this proteolytic molecular machine ...
09-Jan-2011
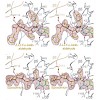
The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of folding, assembly and quality control for proteins of the secretory pathway. The ATP-regulated Hsp70 chaperone BiP (heavy chain–binding protein), together with cochaperones, has important roles in all of these processes. The functional cycle of Hsp70s is determined by conformational transitions that are required for ...
09-Jan-2011

Self-assembled mesoporous structures with well-ordered nano- scale channels could be used in applications such as molecular separation, nano-optics, molecular electronics, nanomedicine and catalysis1–7. However, the domain sizes that can be created in such systems are limited by our lack of a detailed understanding of the relevant growth processes8–12. Here we ...
07-Jan-2011
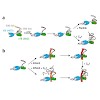
The membrane-integrated transcriptional regulator CadC of Escherichia coli activates expression of the cadBA operon at low external pH with concomitantly available lysine, providing adaptation to mild acidic stress. CadC is a representative of the ToxR-like proteins that combine sensory, signal transduction, and DNA-binding activities within a single polypeptide. ...
05-Jan-2011
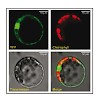
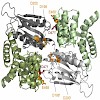
The rd1 natural mutant is one of the first and probably the most commonly studied mouse model for retinitis pigmentosa (RP), a severe and frequently blinding human retinal degeneration. In several decades of research, the link between the increase in photoreceptor cGMP levels and the extremely rapid cell death gave rise to a number of hypotheses. Here, we provide ...
04-Jan-2011

To obtain rates of mRNA synthesis and decay in yeast, we established dynamic transcriptome analysis (DTA). DTA combines non-perturbing metabolic RNA labeling with dynamic kinetic modeling. DTA reveals that most mRNA synthesis rates are around several transcripts per cell and cell cycle, and most mRNA half-lives range around a median of 11 min. DTA can monitor the ...
03-Jan-2011
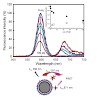
Here we report the synthesis of monofunctional PEGylated amide ligands that were used to prepare bioactivable quantum dots of a 20 nm diameter with a controlled mean number of the covalently grafted ligands. They are stable in aqueous medium of high salinity including a large pH domain
03-Jan-2011

The formation of spider dragline silk is controlled by the relatively small C- and N-terminal domains of the spidroins. The formidable and unrivaled mechanical tensile strength of spider silk fibers is a result of the carefully matched assembly of polyalanine (polyA) or poly(glycinealanine) (polyGA) repeat sequences separated by GGX or GPGXX repeats, which are ...
03-Jan-2011
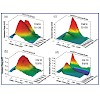
Ultrafast spectroscopy in the visible and midinfrared is used to study the reaction dynamics of two lighttriggered model peptides containing an azobenzene derivative as a switching element. One model peptide, the AzoTrp- Zip2, forms a beta-hairpin structure in the cis form of the chromophore. This peptide is compared to the core structure consisting of the ...
03-Jan-2011

Neurons in cortical sensory regions receive modality-specific information through synapses that are located on their dendrites. Recently, the use of two-photon microscopy combined with whole-cell recordings has helped to identify visually evoked dendritic calcium signals in mouse visual cortical neurons in vivo. The calcium signals are restricted to small ...
01-Jan-2011
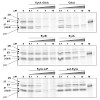
The preparation of a Syringolin A/Glidobactin A hybrid (SylA–GlbA) consisting of a SylA macrocycle connected to the GlbA side chain and its potent proteasome targeting of all three proteasomal subsites is reported. The influence of the syrbactin macrocycle moiety on subsite selectivity is demonstrated.
04-Dec-2010

Protein synthesis occurs in macromolecular particles called ribosomes. All ribosomes are composed of RNA and proteins. While the protein composition of bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes has been well-characterized, a systematic analysis of archaeal ribosomes has been lacking. Here we report the first comprehensive two-dimensional PAGE and mass spectrometry ...
10-Jul-2010
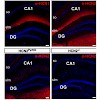
Neuronal hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels are known to modulate spontaneous activity, resting membrane potential, input resistance, afterpotential, rebound activity, and dendritic integration. To evaluate the role of HCN2 for hippocampal synaptic plasticity, we recorded long-term potentiation (LTP) in the direct perforant path ...
05-Jan-2010
The cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) cation channel of rod photoreceptors is a heterotetramer consisting of homologous CNGA1 and CNGB1a subunits. While CNGA1 is indispensable for channel activation, the specific role of CNGB1a in this process has remained elusive. Here, we show that the N-terminal glutamic acid-rich protein (GARP) domain of CNGB1a and soluble GARP2, ...
15-Sep-2006

To register click here to get to the webpage of the CIPSM-Fest of Biological Chemistry 2011 Program of the Scientific Oktoberfest Press release of the Scientific Oktoberfest Pressemitteilung für das Wissenschaftliche Oktoberfest
30-Nov--0001