News 2008
29-Dec-2008
Inhibition or degradation? MicroRNAs have been considered primarily as inhibitors of translation, even though degradation of mRNAs also plays a role in their repressive potential. Two research groups have now quantified the extent to which each mechanism contributes to gene regulation by combining mass spectrometry with transcriptome profiling. The surprising ...
24-Dec-2008
Since the discovery of the proteasome and its structure elucidation intensive research programs in academic institutions and pharmaceutical industries led to identification of a wide spectrum of synthetic and natural small proteasomal inhibitors. Activity studies with these small molecules helped to deeply understand the complex biochemical organization and ...
18-Dec-2008
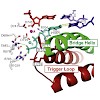
Whereas mechanisms underlying the fidelity of DNA polymerases (DNAPs) have been investigated in detail, RNA polymerase (RNAP) fidelity mechanisms remained poorly understood. New functional and structural studies now suggest how RNAPs select the correct nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) substrate to prevent transcription errors, and how the enzymes detect and remove a ...
18-Dec-2008
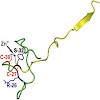
The general subunit of all three eukaryotic RNA polymerases, Rpb12, and subunit P of the archaeal enzyme show sequence similarities in their N-terminal zinc ribbon and some highly conserved residues in the C-terminus. We report here that archaeal subunit P under the control of a strong yeast promoter could complement the lethal phenotype of a RPB12 deletion ...
15-Dec-2008
Electrospray ionization (ESI) of mixtures of organolithium compounds and zinc chloride in tetrahydrofuran produced manifold mono- and polynuclear organozincate anions. Formation of the latter is strongly favored by the incorporation of chloride ligands, which apparently adopt bridging binding modes. Analysis of LinBu/ZnCl2 solutions at different concentrations ...
15-Dec-2008
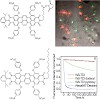
The photophysical properties of three new water-soluble terrylenediimide (WS-TDI) derivatives are investigated and their utilization in biological experiments is demonstrated. Each of these dyes can be excited in the far red region of the visible spectrum, making them good candidates for in-vivo studies. Single-molecule techniques characterize their photophysics ...
12-Dec-2008
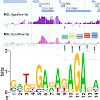
Dosage compensation in male Drosophila relies on the X chromosome–specific recruitment of a chromatin-modifying machinery, the dosage compensation complex (DCC). The principles that assure selective targeting of the DCC are unknown. According to a prevalent model, X chromosome targeting is initiated by recruitment of the DCC core components, MSL1 and MSL2, to a ...
12-Dec-2008

DNA photolyases and cryptochromes (cry) form a family of flavoproteins that use light energy in the blue/UV-A region for the repair of UV-induced DNA lesions or for signaling, respectively. Very recently, it was shown that members of the DASH cryptochrome subclade repair specifically cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) in UV-damaged single-stranded DNA. Here, we ...
12-Dec-2008

y-Secretase is an intramembrane cleaving aspartyl protease complex intimately implicated in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. The protease is composed of the catalytic subunit presenilin (PS1 or PS2), the substrate receptor nicastrin (NCT), and two additional subunits, APH-1 (APH-1a, as long and short splice forms (APH-1aL, APH-1aS), or APH-1b) and PEN-2. Apart ...
11-Dec-2008
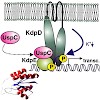
The sensor kinase KdpD and the response regulator KdpE control induction of the kdpFABC operon encoding the high-affinity K+-transport system KdpFABC in response to K+ limitation or salt stress. Under K+ limiting conditions the Kdp system restores the intracellular K+ concentration, while in response to salt stress K+ is accumulated far above the normal content. ...
08-Dec-2008

The “seventeen kilodalton protein” (Skp) is a predominant periplasmic chaperone of Escherichia coli, which is involved in the biogenesis of abundant outer membrane proteins (OMPs) such as OmpA, PhoE, and LamB. In this study the substrate profile of Skp was investigated in a proteomics approach. Skp was overexpressed in a deficient E. coli strain as a fusion ...
04-Dec-2008
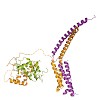
Mediator is a modular multiprotein complex required for regulated transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) II. Here, we show that the middle module of the Mediator core contains a submodule of unique structure and function that comprises the N-terminal part of subunit Med7 (Med7N) and the highly conserved subunit Med31 (Soh1). The Med7N/31 submodule shows a ...
02-Dec-2008
The photoinduced electrocyclic ring-opening of a fluorinated indolylfulgide is investigated by stationary and ultrafast spectroscopy in the UV/vis spectral range. Photoreactions, initiated by optical excitation into the S1 (570 nm) and SN (340 nm) absorption band of the closed isomer, lead to considerable differences in reaction dynamics and quantum yields. ...
01-Dec-2008
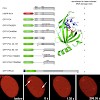
The multifunctional nuclear protein positive cofactor 4 (PC4) is involved in various cellular processes including transcription, replication, and chromatin organization. Recently, PC4 has been identifi ed as a suppressor of oxidative mutagenesis in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae . To investigate a potential role of PC4 in mammalian DNA repair, we ...
01-Dec-2008

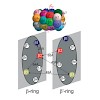
We have studied the initial phase of cell adhesion as a function of the lateral organization of individual integrin molecules with single-cell force microscopy. Nanostructures, consisting of hexagonally ordered gold dots, were prepared with diblock-copolymer micelle lithography and functionalized with arginine- glycine-aspartate peptides, thus defining integrin ...
25-Nov-2008

YEAH! CIPSM ist „Ausgewählter Ort im Land der Ideen“. Damit ist CIPSM Teil der Veranstaltungsreihe „365 Orte im Land der Ideen“, die gemeinsam von der Standortinitiative „Deutschland – Land der Ideen“ und der Deutschen Bank durchgeführt wird. Als „Ausgewählter Ort“ wird CIPSM unter der Schirmherrschaft von Bundespräsident Horst Köhler im Jahr 2009 Deutschland als ...
21-Nov-2008

Small noncoding RNAs function in concert with Argonaute (Ago) proteins to regulate gene expression at the level of transcription, mRNA stability, or translation. Ago proteins bind small RNAs and form the core of silencing complexes. Here,wereport the analysis of small RNAs associated with human Ago1 and Ago2 revealed by immunoprecipitation and deep sequencing. ...
20-Nov-2008

The maintenance of progenitor cells is a crucial aspect of central nervous system development and maturation, and bHLH transcription factors of the E(Spl) subfamily are involved in this process in all vertebrates studied to date. In the zebrafish embryonic neural plate, a large number of E(Spl) genes (her genes) are at play.We review recent data on this point, ...
18-Nov-2008

The TIM23 complex is the major translocase of the mitochondrial inner membrane responsible for the import of essentially all matrix proteins and a number of inner membrane proteins. Tim23 and Tim50, two essential proteins of the complex, expose conserved domains into the intermembrane space which interact with each other. Here, we describe in vitro reconstitution ...
17-Nov-2008

We provide a protocol that describes an explant system that allows the dynamics of motor axons to be imaged. This method is based on nerve–muscle explants prepared from the triangularis sterni muscle of mice, a thin muscle that covers the inside of the thorax. These explants, which can be maintained alive for several hours, contain long stretches of peripheral ...
14-Nov-2008
An investigation of the precise interactions between damaged DNA and DNA repair enzymes is required in order to understand the lesion recognition step, which is one of the most fundamental processes in DNA repair. Most recently, photoaffinity labeling approaches have enabled the analysis of even transient protein- DNA interactions. Here we report the synthesis ...
13-Nov-2008
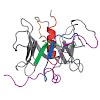
Motivation: Phospholipid scramblases (PLSCRs) constitute a family of cytoplasmic membrane-associated proteins that were identified based upon their capacity to mediate a Ca2+-dependent bidirectional movement of phospholipids across membrane bilayers, thereby collapsing the normally asymmetric distribution of such lipids in cell membranes. The exact function and ...
10-Nov-2008
The activation of well-defined numbers of integrin molecules in predefined areas by adhesion of tissue cells to biofunctionalized micro-nanopatterned surfaces was used to determine the minimum number of activated integrins necessary to stimulate focal adhesion formation. This was realized by combining micellar and conventional e-beam lithography, which enabled ...
10-Nov-2008
Serotonin is a major central nervous modulator of physiology and behavior and plays fundamental roles during development and plasticity of the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Understanding the developmental control and functions of serotonergic neurons is therefore an important task. In all vertebrates, prominent serotonergic neurons are found in the ...
10-Nov-2008
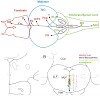
Serotonin is a major central nervous modulator of physiology and behavior and plays fundamental roles during development and plasticity of the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Understanding the developmental control and functions of serotonergic neurons is therefore an important task. In all vertebrates, prominent serotonergic neurons are found in the ...
06-Nov-2008

Large-scale analysis directly at the protein level holds the promise of uncovering features not apparent or present at the gene level [1,2,3]. Although mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics can now identify and quantify thousands of cellular proteins in large-scale proteomics experiments, much of the peptide information contained in these experiments remains ...
05-Nov-2008
Structural investigations are frequently hindered by difficulties in obtaining diffracting crystals of the target protein. Here, we report the crystallization and structure solution of the U2AF homology motif (UHM) domain of splicing factor Puf60 fused to Escherichia coli thioredoxin A. Both modules make extensive crystallographic contacts, contributing to a ...
05-Nov-2008

Tic110 has been proposed to be a channel-forming protein at the inner envelope of chloroplasts whose function is essential for the import of proteins synthesized in the cytosol. Sequence features and topology determination experiments presently summarized suggest that Tic110 consists of six transmembrane helices. Its topology has been mapped by limited ...
04-Nov-2008
The incorporation of proline into cyclic peptides seems to be the most promising way to induce -turn structures. Recently, however, it was shown that N-methylated amino acids might be even better suited than proline for introducing turn structures. Another property of proline, the ability to effect cis-peptide bonds, has also been reported for N-methylated amino ...
02-Nov-2008
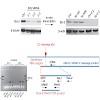
Genetic and epigenetic plasticity allows tumors to evade single-targeted treatments. Here we direct Bcl2-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) with 5¢-triphosphate ends (3p-siRNA) against melanoma. Recognition of 5¢-triphosphate by the cytosolic antiviral helicase retinoic acid–induced protein I (Rig-I, encoded by Ddx58) activated innate immune cells such as ...
02-Nov-2008
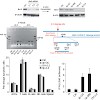
Genetic and epigenetic plasticity allows tumors to evade single-targeted treatments. Here we direct Bcl2-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) with 5¢-triphosphate ends (3p-siRNA) against melanoma. Recognition of 5¢-triphosphate by the cytosolic antiviral helicase retinoic acid–induced protein I (Rig-I, encoded by Ddx58) activated innate immune cells such as ...
02-Nov-2008
Genetic and epigenetic plasticity allows tumors to evade single-targeted treatments. Here we direct Bcl2-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) with 5¢-triphosphate ends (3p-siRNA) against melanoma. Recognition of 5¢-triphosphate by the cytosolic antiviral helicase retinoic acid–induced protein I (Rig-I, encoded by Ddx58) activated innate immune cells such as ...
01-Nov-2008
Viscotoxins are small cationic proteins found in European mistletoe Viscum album. They are highly toxic towards phytopathogenic fungi and cancer cells. Heterologous expression of viscotoxins would broaden the spectrum of methods to be applied for better understanding of their structure and function and satisfy possible biopharmaceutical needs. Here, we evaluated ...
31-Oct-2008

Photochemical solar energy conversion is considered as an alternative of clean energy. For future light converting nano-machines photosynthetic reaction centers are used as prototypes optimized during evolution. We introduce a reaction scheme for global optimization and simulate the ultrafast charge separation in photochemical energy conversion. Multiple ...
30-Oct-2008

Specific interactions of transmembrane helices play a pivotal role in the folding and oligomerization of integral membrane proteins. The helix–helix interfaces frequently depend on specific amino acid patterns. In this study, a heptad repeat pattern was randomized with all naturally occurring amino acids to uncover novel sequence motifs promoting transmembrane ...
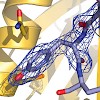
29-Oct-2008
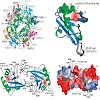
PUF60 is an essential splicing factor functionally related and homologous to U2AF65. Its C-terminal domain belongs to the family of U2AF (U2 auxiliary factor) homology motifs (UHM), a subgroup of RNA recognition motifs that bind to tryptophan-containing linear peptide motifs (UHM ligand motifs, ULMs) in several nuclear proteins. Here, we show that the Puf60 UHM ...
28-Oct-2008
The metabotropic glutamate receptors type 1 (mGluR1s) are required for a normal function of the mammalian cerebellum. These G-protein-coupled receptors are abundantly expressed in the principle cerebellar cells, namely the Purkinje neurones. Under physiological conditions, mGluR1s are activated during repetitive activity of both afferent glutamatergic synaptic ...
27-Oct-2008

UV irradiation of cells gives rise to the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) and so-called (6-4) DNA lesions (Scheme 1). Both lesions are major photoproducts formed in dipyrimidine sequences of double-stranded DNA. Repair of these lesions is essential because of their high mutagenic potential. Particularly important in many organisms are the ...
25-Oct-2008

Dendritic cell (DC) vaccines have emerged as a promising strategy to induce antitumoral cytotoxic T cells for the immunotherapy of cancer. The maturation state of DC is of critical importance for the success of vaccination, but the most effective mode of maturation is still a matter of debate. Whereas immature DC carry the risk of inducing tolerance, extensive ...
24-Oct-2008
Messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs) move randomly within nucleoplasm before they exit from the nucleus. To further understand mRNP trafficking, we have studied the intranuclear movement of a specific mRNP, the BR2 mRNP, in salivary gland cells in Chironomus tentans. Their polytene nuclei harbor giant chromosomes separated by vast regions of nucleoplasm, ...
21-Oct-2008

We have recently identified the archaic cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a non-canonical ligand of the CXC chemokine receptors CXCR2 and CXCR4 in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Because its affinity for CXCR2 was particularly high, we hypothesized that MIF may feature structural motives shared by canonical CXCR2 ligands, ...
21-Oct-2008
Salinosporamide A (1 (NPI-0052)) is a potent, monochlorinated 20S proteasome inhibitor in clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. To elucidate the role of the chlorine leaving group (LG), we synthesized analogues with a range of LG potentials and determined their IC50 values for inhibition of chymotrypsin-like (CT-L), trypsin-like (T-L), and caspase-like ...
21-Oct-2008
The structure of the extracellular domain of BMP receptor IA was determined in solution by NMR spectroscopy and compared to its structure when bound to its ligand BMP-2. While most parts of the secondary structure are highly conserved between the bound and unbound forms, large conformational rearrangements can be observed in the b4b5 loop of BMPR-IA, which is in ...
21-Oct-2008
Our long-term goal is the in vivo expression of intrinsically colored proteins without the need for further posttranslational modification or chemical functionalization by externally added reagents. Biocompatible (Aza)Indoles (Inds)/(Aza)Tryptophans (Trp) as optical probes represent almost ideal isosteric substitutes for natural Trp in cellular proteins. To ...
20-Oct-2008

The identification of interaction partners in protein complexes is a major goal in cell biology. Here we present a reliable affi nity purifi cation strategy to identify specifi c interactors that combines quantitative SILAC-based mass spectrometry with characterization of common contaminants binding to affi nity matrices (bead proteomes). This strategy can be ...
17-Oct-2008

We are very happy that Ulrike Gaul, professor of molecular biology at Rockefeller University New York, will join CIPSM at the Gene Center in 2009 as a newly established CIPSM full professor. This CIPSM professorship for molecular systems biology has been selected for the first Alexander von Humboldt professorship ever to be awarded and comes with an prize money ...
17-Oct-2008
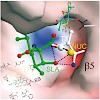
Spiro β-lactone-based proteasome inhibitors were discovered in the context of an asymmetric catalytic total synthesis of the natural product (+)-lactacystin (1). Lactone 4 was found to be a potent inhibitor of the 26S proteasome, while its C-6 epimer (5) displayed weak activity. Crystallographic studies of the two analogues covalently bound to the 20S proteasome ...
17-Oct-2008
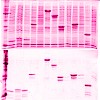
Viscotoxins are small cationic proteins found in European mistletoe Viscum album. They are highly toxic towards phytopathogenic fungi and cancer cells. Heterologous expression of viscotoxins would broaden the spectrum of methods to be applied for better understanding of their structure and function and satisfy possible biopharmaceutical needs. Here, we evaluated ...
17-Oct-2008
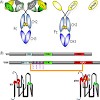
It is well established that all camelids have unique antibodies circulating in their blood. Unlike antibodies fromother species, these special antibodies are devoid of light chains and are composed of a heavy-chainhomodimer. These so-called heavy-chain antibodies (HCAbs) are expressed after a V–D–J rearrangement and require dedicated constant g-genes. An immune ...
14-Oct-2008

The winners of the second ever Innovation Award of the German BioRegions were announced on the 7th October – Thomas Böttcher together with Dr. Stephan Sieber from CIPSM were awarded joint prizes by Director General from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research together with Dr. Heinz Bettmann, BioCologne e.V. representing this year’s sponsors. The ...
13-Oct-2008

Proteins are often modified posttranslationally by glycosylation and lipidation. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors combine both types of modification and link many proteins to the cell surface. Advances in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and recombinant protein engineering, in combination with the development of native chemical ligation (NCL) and ...
12-Oct-2008
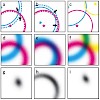
Very often, the positions of flexible domains within macromolecules as well as within macromolecular complexes cannot be determined by standard structural biology methods. To overcome this problem, we developed a method that uses probabilistic data analysis to combine single-molecule measurements with X-ray crystallography data. The method determines not only the ...
11-Oct-2008
With the evolution of multidrug resistant bacterial pathogens, infectious diseases pose once again a serious threat to public health. Especially the opportunistic pathogen Staphylococcus aureus has gained importance through the dramatically increasing appearance of methicillin-resistant (MRSA) strains in hospitals and the recent emergence of epidemic ...
06-Oct-2008
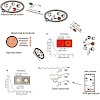
In this study we analyze 5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT]; serotonin) signaling in zebrafish, an increasingly popular vertebrate disease model. We compare and contrast expression of the 5-HT transporter genes slc6a4a and slc6a4b, which identify 5-HT-producing neurons and three novel 5-HT receptors, htr1aa, htr1ab, and htr1bd. slc6a4a and slc6a4b are expressed in the ...
06-Oct-2008
Perdeuterated poly(styrene) is introduced as an almost artefactfree and arbitrarily scalable alignment medium for measuring residual dipolar couplings and other anisotropic NMR parameters; the spectral quality achievable in this new medium is demonstrated for HSQC spectra leading to the conformational analysis of staurosporine and homonuclear TOCSY-type experiments.
01-Oct-2008
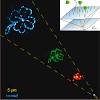
Self-assembly guided by molecular recognition has in the past been employed to assemble nanoparticle superstructures like hypercrystals or nanoparticle molecules. An alternative approach, the direct molecule-by-molecule assembly of nanoscale superstructures, was demonstrated recently. Here we present a hybrid approach where we first assemble a pattern of binding ...
01-Oct-2008
Despite their abundance, still little is known about the rather frequent, constantly proliferating progenitors spread throughout the adult mouse brain parenchyma. The majority of these progenitors express the basic-helix-loop-helix transcription factor Olig2, and their number further increases after injury. Here, we examine the progeny of this progenitor ...
22-Sep-2008
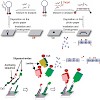
The attachment of labels onto DNA is of utmost importance in many areas of biomedical research and is valuable in the construction of DNA-based functional nanomaterials. The copper(I)-catalyzed Huisgen cycloaddition of azides and alkynes (CuAAC) has recently been added to the repertoire of DNA labeling methods, thus allowing the virtuallyunlimited ...
19-Sep-2008
The neurodegeneration observed in Alzheimer’s disease has been associated with synaptic dismantling and progressive decrease in neuronal activity. We tested this hypothesis in vivo by using two-photon Ca2+ imaging in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Although a decrease in neuronal activity was seen in 29% of layer 2/3 cortical neurons, 21% of neurons ...
16-Sep-2008
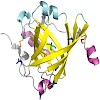
α1-Acid glycoprotein (AGP) is an important drug-binding protein in human plasma and, as an acute-phase protein, it has a strong influence on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of many pharmaceuticals. We report the crystal structure of the recombinant unglycosylated human AGP at 1.8 Å resolution, which was solved using the new method of UVradiation- ...
11-Sep-2008
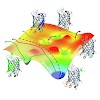
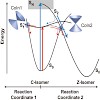
The directed application of force to different points on the surface of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) makes it possible to shift between two different pathways with distinct unfolding intermediates. One pathway resembles a “folding-like” pathway, whereas the other may play a role during processes such as import through a pore. The picture shows the energy ...
10-Sep-2008
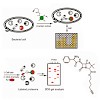
With the development of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains, infectious diseases have become again a life-threatening problem. One of the reasons for this dilemma is the limited number and breadth of current therapeutic targets for which several resistance strategies have evolved over time. To expand the number of addressable enzyme targets and to understand ...
10-Sep-2008

2008 is great! Ein hochrangiger Wissenschaftler kündigt seine Stelle an der Eliteuniversität Berkeley, weil er lieber an einer deutschen Universität arbeiten möchte - und bringt auch gleich sein ganzes Forschungsteam mit. pdf link
05-Sep-2008

Nonproteinogenic amino acids that either occur naturally or are synthesized chemically are becoming important tools in modern drug discovery. In this context, fluorinated amino acids have great potential in the development of novel pharmaceuticals and drugs. To assess whether different fluorinated aromatic amino acid analogues of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and ...
05-Sep-2008

RNA interference is a powerful way to study gene function and is frequently combined with microarray analysis. Here we introduce a similar technology at the protein level by simultaneously applying Stable Isotope Labeling by Amino acids in Cell culture (SILAC) and RNA interference (RNAi) to Drosophila SL2 cells. After knockdown of ISWI, an ATP-hydrolyzing motor ...
03-Sep-2008

Biological responses to mechanical stress require strain-sensing molecules, whose mechanically induced conformational changes are relayed to signaling cascades mediating changes in cell and tissue properties. In vertebrate muscle, the giant elastic protein titin is involved in strain sensing via its C-terminal kinase domain (TK) at the sarcomeric M-band and ...
03-Sep-2008
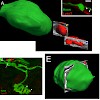
Clearance of cellular debris is a critical feature of the developing nervous system, as evidenced by the severe neurological consequences of lysosomal storage diseases in children. An important developmental process, which generates considerable cellular debris, is synapse elimination, in which many axonal branches are pruned. The fate of these pruned branches is ...
03-Sep-2008

More than one hundred and fifty familial Alzheimer's Disease (FAD)-associated missense mutations in presenilins (PS1 and PS2), the catalytic subunit of the γ- secretase complex, cause aberrant Amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) production, by increasing the relative production of the highly amyloidogenic 42 amino acid variant. The molecular mechanism behind this pathological ...
30-Aug-2008

The oxazolidinones represent the first new class of antibiotics to enter into clinical usage within the past 30 years, but their binding site and mechanism of action has not been fully characterized. We have determined the crystal structure of the oxazolidinone linezolid bound to the Deinococcus radiodurans 50S ribosomal subunit. Linezolid binds in the A site ...
27-Aug-2008
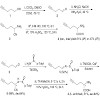
An improved classic Strecker synthesis was elaborated leading to racemic homopropargylglycine (Hpg) in 61% overall yield, while an asymmetric Strecker reaction produced Hpg and the higher homolog 2-aminohept-6-ynoic acid in significantly higher yields and over 80% ee.
26-Aug-2008
in the past decade, the potential of harnessing the ability of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMr) spectroscopy to monitor intermolecular interactions as a tool for drug discovery has been increasingly appreciated in academia and industry. in this Perspective, we highlight some of the major applications of NMR in drug discovery, focusing on hit and lead generation, ...
25-Aug-2008
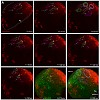
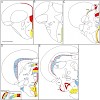
Neuronal production in the midbrain-hindbrain domain (MH) of the vertebrate embryonic neural tube depends on a progenitor pool called the ‘intervening zone’ (IZ), located at the midbrain-hindbrain boundary. The progressive recruitment of IZ progenitors along the mediolateral (future dorsoventral) axis prefigures the earlier maturation of the MH basal plate. It ...
22-Aug-2008

CIPSM Coordinator Horst Kessler wins 2008 Joseph Rudinger Award of the European Peptide Society for his lifetime achievements in peptide chemistry! The Joseph Rudinger Award award is presented „in commemoration of Josef Rudinger’s role in the foundation of the European Peptide Symposia and of the diverse contributions he made to peptide chemistry.” We thank and ...
22-Aug-2008
Protein-protein interactions regulate almost all aspects of cellular signaling and aberrant protein-protein interactions have the potential to cause or contribute to human disease. The modulation of these interactions by drug-like molecules would offer previously unavailable opportunities to explore the relevance of pre-selected protein-protein interactions for ...
22-Aug-2008
Imprinted genes are important in development and their allelic expression is mediated by imprinting control regions (ICRs). On their DNA-methylated allele, ICRs are marked by trimethylation at H3 Lys 9 (H3K9me3) and H4 Lys 20 (H4K20me3), similar to pericentric heterochromatin. Here, we investigate which histone methyltransferases control this methylation of ...
19-Aug-2008
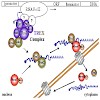
CIPSM-Junior-Group Leader Katja Sträßer has done it! She received a grant of nearly one million Euros from the European Research Council for the next five years. She will explore the understanding of a new aspect of how genetic information is read out by a cell. Many of the individual steps examined separately in the past are coupled with each other to allow for ...
17-Aug-2008
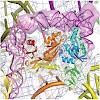
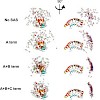
EF4 (LepA) is an almost universally conserved translational GTPase in eubacteria. It seems to be essential under environmental stress conditions and has previously been shown to back-translocate the tRNAs on the ribosome, thereby reverting the canonical translocation reaction. In the current work, EF4 was directly visualized in the process of back-translocating ...
14-Aug-2008

In the mammalian central nervous system, slow synaptic excitation involves the activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). It has been proposed that C1-type transient receptor potential (TRPC1) channels underlie this synaptic excitation, but our analysis of TRPC1-deficient mice does not support this hypothesis. Here, we show unambiguously that it is ...
14-Aug-2008
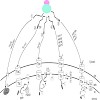
The chloroplast inner envelope membrane contains many integral proteins which differ in the number of a-helices that anchor the protein into the bilayer. For most of these proteins it is not known which pathway they engage to reach their final localisation within the membrane. In yeast mitochondria, two distinct sorting/insertion pathways have been described for ...
13-Aug-2008

The orphan nuclear receptor NR4A2/Nurr1 is mandatory for the terminal differentiation of mesencephalic dopamine neurons in mammals, but a similar role has remained elusive in the homologous area of the fish brain, the posterior tuberculum. Using loss- and gain-of-function experiments in zebrafish, we show that NR4A2 is indeed responsible for the expression of ...
08-Aug-2008
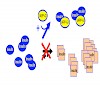
In vivo protein aggregation is strongly linked to the pathogenesis of several incurable celland neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and type II diabetes (T2D). In vitro protein aggregation leads to a loss of function and complicates therapeutic application of a number of bioactive proteins or polypeptides such as insulin. Designing ...
04-Aug-2008

What is rheology? Most people are familiar with the basics of rheology from experience with diarrhea or perhaps rheostats. The word rheology was invented in 1929 to name the discipline of a society engaged in the study of how materials deform in response to forces. It was inspired by a quote by Heraclitus: “παντα ρει” translated as “everything flows”. Indeed ...
04-Aug-2008

Biomimetic synthesis is an attempt to assemble natural products along biosynthetic lines without recourse to the full enzymatic machinery of nature. We exemplify this with a total synthesis of exiguamine A and the newly isolated natural product exiguamine B. The most noteworthy feature of this work is an oxidative endgame drawing from the complex chemistry of ...
01-Aug-2008
We present the implementation of a target function based on Small Angle Scattering data (Gabel et al. Eur Biophys J 35(4):313–327, 2006) into the Crystallography and NMR Systems (CNS) and demonstrate its utility in NMR structure calculations by simultaneous application of small angle scattering (SAS) and residual dipolar coupling (RDC) restraints. The efficiency ...
01-Aug-2008
SNARE proteins mediate fusion of intracellular eukaryotic membranes and their -helical transmembrane domains are known to contribute to lipid bilayer mixing. Synthetic transmembrane domain peptides were previously shown to mimic the function of SNARE proteins in that they trigger liposome fusion in a sequence-specific fashion. Here, we performed a detailed ...
30-Jul-2008
Selected residues of transmembrane domain (TM) IX were previously shown to play key roles in ligand binding and transport in members of the Na+/solute symporter family. Using the Na+/proline transporter PutP as a model, a complete Cys scanning mutagenesis of TM IX (positions 324 to 351) was performed here to further investigate the functional significance of the ...
30-Jul-2008

Yeast RNA polymerase (Pol) II consists of a 10-subunit core enzyme and the Rpb4/7 subcomplex, which is dispensable for catalytic activity and dissociates in vitro. To investigate whether Rpb4/7 is an integral part of DNA-associated Pol II in vivo, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled to high resolution tiling microarray analysis. We show that the ...
30-Jul-2008
The spore photoproduct is a unique photolesion, formed in spores upon irradiation with UV light; to investigate the properties of spore photoproduct containing DNA we have synthesized 5S and 5R lesion analogs and incorporated them into DNA.
29-Jul-2008
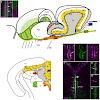
The zebrafish adult brain contains numerous neural progenitors and is a good model to approach the general mechanisms of adult neural stem cell maintenance and neurogenesis. Here we use this model to test for a correlation between Fgf signaling and cell proliferation in adult progenitor zones. We report expression of Fgf signals (fgf3,4,8a,8b,17b), receptors ...
23-Jul-2008
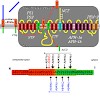
Gamma-Secretase mediates the final proteolytic cleavage, which liberates Amyloid beta -peptide, the major component of senile plaques in the brain of Alzheimer's disease patients. Therefore gamma -secretase is a prime target for Amyloid beta -peptide lowering therapeutic strategies. gamma -Secretase is a protein complex composed of four different subunits, ...
22-Jul-2008

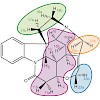
U2AF homology motifs (UHM) are protein domains that bind peptidic UHM ligand motifs (ULM) and thus form an intricate network of interactions involved in splicing regulation. Here, we report the backbone assignment of the UHM domain of the splicing factor Puf60 as well as 1H, 15N chemical shifts upon binding of the ULM peptides U2AF65 (85–112), SF1 (1–25), SF3b155 ...
Fpg (MutM) recognizes bulky N7-substituted-FapydG lesion using a novel and unproductive binding mode
21-Jul-2008
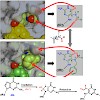
Fpg (MutM) is a bacterial base excision repair enzyme that removes the mutagenic and/or replication-block lesions 8-oxoguanine (8-oxodG) and imidazole-ring opened purines (Fapy-derivatives) from DNA. This work shows that Fpg and its eukaryote homologue Ogg1 recognize with high affinity FapydG and bulky N7-benzyl-FapydG (Bz-FapydG). The comparative crystal ...
18-Jul-2008
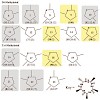
The potential of peptides as drug candidates is limited by their poor pharmacokinetic properties. Many peptides have a short half-life in vivo and a lack of oral availability. Inspired by the excellent pharmacokinetic profile of cyclosporine, a natural, multiply N-methylated cyclic peptide, we envisioned multiple N-methylation as a promising way to rationally ...
12-Jul-2008
Genetic high-throughput screens have yielded large sets of potential protein-protein interactions now to be verified and further investigated. Here we present a simple assay to directly visualize protein-protein interactions in single living cells. Using a modified lac repressor system, we tethered a fluorescent bait at a chromosomal lac operator array and ...
12-Jul-2008
Mitochondria are essential organelles of the eukaryotic cells that are made by expansion and division of pre-existing mitochondria. The majority of their protein constituents are synthesized in the cytosol. They are transported into and put together within the organelle. This complex process is facilitated by several protein translocases. Here we summarize ...
09-Jul-2008

Actin belongs to the most abundant proteins in eukaryotic cells which harbor usually many conventional actin isoforms as well as actin-related proteins (Arps). To get an overview over the sometimes confusing multitude of actins and Arps, we analyzed the Dictyostelium discoideum actinome in detail and compared it with the genomes from other model organisms. The D. ...
02-Jul-2008
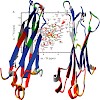
Folding intermediates play a key role in defining protein folding and assembly pathways as well as those of misfolding and aggregation. Yet, due to their transient nature, they are poorly accessible to high-resolution techniques. Here, we made use of the intrinsically slow folding reaction of an antibody domain to characterize its major folding intermediate in ...
01-Jul-2008

The precise coordination of the different steps of DNA replication is critical for the maintenance of genome stability. We have probed the mechanisms coupling various components of the replication machinery and their response to polymerase stalling by inhibition of the DNA polymerases in living mammalian cells with aphidicolin. We observed little change in the ...
01-Jul-2008
In the current issue of Nature Medicine, Faghihi et al. report that a noncoding antisense RNA against β-secretase, also known as BACE1 (β-site amyloid precursor protein (APP)-cleaving enzyme), may contribute to pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. BACE1 is a vertebrate-specific enzyme, which, together with presenilin-dependent γ-secretase, cleaves APP to generate ...
21-Jun-2008
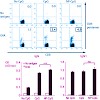
Viral nucleic acids are recognized by specific pattern-recognition receptors of the Toll-like and RIG-I-like receptor families. Synthetic DNA and RNA oligonucleotides can activate the immune system through these receptors and potentiate Ab and CD8 cytotoxic responses to Ags. Systemic application of immunostimulatory oligonucleotides however also results in a ...
20-Jun-2008

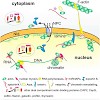
Cytoplasmic localization and localized translation of messenger RNAs contribute to asymmetrical protein distribution. Recognition of localized mRNAs by RNA-binding proteins can occur in the cytoplasm or, alternatively, co- or post-transcriptionally in the nucleus. In budding yeast, mRNAs destined for localization are bound by the She2 protein before their nuclear ...
18-Jun-2008

Cell interactions with adhesive surfaces play a vital role in the regulation of cell proliferation, viability, and differentiation, and affect multiple biological processes. Since cell adhesion depends mainly on the nature and density of the adhesive ligand molecules, spatial molecular patterning, which enables the modulation of adhesion receptor clustering, ...
13-Jun-2008
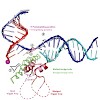
To study how RNA polymerase II translocates after nucleotide incorporation, we prepared elongation complex crystals in which pre- and post-translocation states interconvert. Crystal soaking with the inhibitor alpha-amanitin locked the elongation complex in a new state, which was refined at 3.4-Å resolution and identified as a possible translocation intermediate. ...
09-Jun-2008

The inhibition of integrin function is a major challenge in medicinal chemistry. Potent ligands are currently in different stages of clinical trials for the antiangiogenic therapy of cancer and agerelated macula degeneration (AMD). The subtype a5b1has recently been drawn into the focus of research because of its genuine role in angiogenesis. In our previous work ...
07-Jun-2008
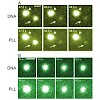
Endosomal escape is a well-known bottleneck for successful delivery of macromolecular drugs and genes. Photochemical disruption of endosomal membranes is an approach to overcome this bottleneck. In this study, we used the photosensitizer disulphonated meso-tetraphenylporphine with sulfonate groups on adjacent phenyl rings (TPPS2a) to investigate photoinduced ...
06-Jun-2008

Fluorescence light microscopy allows multicolor visualization of cellular components with high specificity, but its utility has until recently been constrained by the intrinsic limit of spatial resolution. We applied three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM) to circumvent this limit and to study the mammalian nucleus. By simultaneously imaging ...
31-May-2008

Thioxoamide (thioamide) bonds are nearly isosteric substitutions for amides but have altered hydrogen-bonding and photophysical properties. They are thus well-suited backbone modifications for physicochemical studies on peptides and proteins. The effect of thioxoamides on protein structure and stability has not been subject to detailed experimental investigations ...
30-May-2008
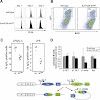
H4K20 methylation is a broad chromatin modification that has been linked with diverse epigenetic functions. Several enzymes target H4K20 methylation, consistent with distinct mono-, di-, and trimethylation states controlling different biological outputs. To analyze the roles of H4K20 methylation states, we generated conditional null alleles for the two Suv4-20h ...
28-May-2008
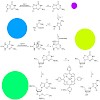
Imidazolone (dIz) is an abundant, highly mutagenic, and rather unstable DNA lesion that can cause dG!dC transversion mutations. dIz is generated in DNA by a variety of oxidative processes such as type I photooxidation. Herein we report the synthesis of a carbocyclic nucleoside analogue of dIz and of DNA containing this stabilized lesion analogue. The carbocyclic ...
28-May-2008

Heterochromatic chromosomal regions undergo large-scale reorganization and progressively aggregate, forming chromocenters. These are dynamic structures that rapidly adapt to various stimuli that influence gene expression patterns, cell cycle progression, and differentiation. Np95-ICBP90 (m- and h-UHRF1) is a histone-binding protein expressed only in proliferating ...
22-May-2008
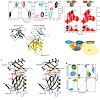
Targeted protein degradation is largely performed by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, in which substrate proteins are marked by covalently attached ubiquitin chains that mediate recognition by the proteasome. It is currently unclear how the proteasome recognizes its substrates, as the only established ubiquitin receptor intrinsic to the proteasome is Rpn10/S5a ...
22-May-2008
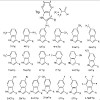
Non-canonical amino acids (NAA), as building blocks for peptides and proteins during ribosomal translation, represent a nearly infinite supply of novel functions. The specific selection, activation and tRNA-charging of amino acids by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (AARS) in the aminoacylation reaction are essential steps. In most cases, aminoacylation of NAA is a ...
21-May-2008
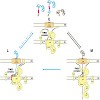
The TIM23 (translocase of the mitochondrial inner membrane) complex mediates translocation of preproteins across and their insertion into the mitochondrial inner membrane. How the translocase mediates sorting of preproteins into the two different subcompartments is poorly understood. In particular, it is not clear whether association of two operationally defined ...
19-May-2008

The serine/threonine kinase polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is critically involved in multiple mitotic processes and has been established as an adverse prognostic marker for tumor patients. Plk1 localizes to its substrates and its intracellular anchoring sites via its polo-box domain (PBD), which is unique to the family of polo-like kinases. Therefore, inhibition of ...
19-May-2008
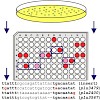
Photorhabdus luminescens is a Gram-negative luminescent enterobacterium and a symbiote to soil nematodes belonging to the species Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. P.luminescens is simultaneously highly pathogenic to insects. This bacterium exhibits a complex life cycle, including one symbiotic stage characterized by colonization of the upper nematode gut, and a ...
16-May-2008
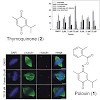
The serine/threonine kinase Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is overexpressed in many types of human cancers, and has been implicated as an adverse prognostic marker for cancer patients. Plk1 localizes to its intracellular anchoring sites via its polo-box domain (PBD). Here we show that Plk1 can be inhibited by small molecules which interfere with its intracellular ...
09-May-2008
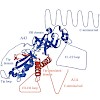
The removal of flexible protein regions is generally used to promote crystallization, but advanced strategies to quickly remove multiple flexible regions from proteins or protein complexes are lacking. Here, it is shown how a protein heterodimer with multiple flexibilities, the RNA polymerase I subcomplex A14/A43, could be crystallized with the use of an ...
09-May-2008
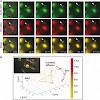
Intracellular mRNA localization is a common mechanism to achieve asymmetric distributions of proteins. Previous studies have revealed that in a number of cell types, differentmRNA species are localized by the same transport machinery. However, it has been unclear if these individual mRNA species are specifically sorted into separate or common ribonucleoprotein ...
08-May-2008

In higher eukaryotes, an unusual C-terminal domain (CTD) is crucial to the function of RNA polymerase II in transcription. The CTD consists of multiple heptapeptide repeats; differences in the number of repeats between organisms and their degree of conservation have intrigued researchers for two decades. Here, we review the evolution of the CTD at the molecular ...
07-May-2008
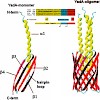
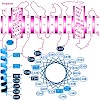
The Oca family is a novel class of autotransporter-adhesins with highest structural similarity in their C-terminal transmembrane region, which supposedly builds a beta-barrel pore in the outer membrane (OM). The prototype of the Oca family is YadA, an adhesin of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. YadA forms a homotrimeric lollipop-like ...
27-Apr-2008

Fluorescent proteins (FP) are widely used as in vivo reporter molecules and are available in multiple colors spanning almost the entire visible light spectrum. Genetically fused to any protein target, FPs offer a powerful tool to study protein localization and dynamics. After the isolation of the prototypical green fluorescent protein (GFP) from the jellyfish ...
26-Apr-2008
In this article, we follow the history of one of the most abundant, most intensely studied proteins of the eukaryotic cells: actin. We report on hallmarks of its discovery, its structural and functional characterization and localization over time, and point to present days’ knowledge on its position as a member of a large family. We focus on the rather puzzling ...
25-Apr-2008
Identifying independently folding cores or substructures is important for understanding and assaying the structure, function and assembly of large proteins. Here, we suggest mechanical stability as a criterion to identify building blocks of the 366 amino acid maltose-binding protein (MBP). We find that MBP, when pulled at its termini, unfolds via three (meta-) ...
The Role of 23S Ribosomal RNA Residue A2451 in Peptide Bond Synthesis Revealed by Atomic Mutagenesis
24-Apr-2008
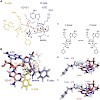
Peptide bond formation is a fundamental reaction in biology, catalyzed by the ribosomal peptidyl-transferase ribozyme. Although all active-site 23S ribosomal RNA nucleotides are universally conserved, atomic mutagenesis suggests that these nucleobases do not carry functional groups directly involved in peptide bond formation. Instead, a single ribose 20-hydroxyl ...
24-Apr-2008
Introducing point mutations into bacterial chromosomes is important for further progress in studies relying on functional genomics, systems- and synthetic biology, and for metabolic engineering. For many investigations, chromosomal systems are required rather than artificial plasmid based systems. Here we describe the introduction of a single point mutation into ...
24-Apr-2008
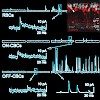
Synaptic integration is modulated by inhibition onto the dendrites of postsynaptic cells. However, presynaptic inhibition at axonal terminals also plays a critical role in the regulation of neurotransmission. In contrast to the development of inhibitory synapses onto dendrites, GABAergic/glycinergic synaptogenesis onto axon terminals has not been widely studied. ...
22-Apr-2008
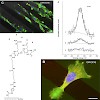
With the advances made in surface patterning by micro- and nanotechnology, alternative methods to immobilize biomolecules for different purposes are highly desired. RGD peptides are commonly used to create cell-attractive surfaces for cell-biological and also medical applications. We have developed a fast, one-step method to bind RGD peptides covalently to ...
22-Apr-2008
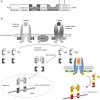
Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) are a family of transcription factors that are of central importance for cellular signaling and have therefore emerged as attractive target proteins for cell-permeable small molecules. This review outlines the basic concept of STAT signaling, the relevance of individual members of the STAT family for ...
17-Apr-2008

The multisubunit RNA polymerases (Pols) II and III synthesize mainly eukaryotic mRNAs and tRNAs, respectively. Pol II and Pol III are protein complexes consisting of 12 and 17 subunits. Here we analyzed both yeast Pol II and Pol III by multiplexed mass spectrometric analysis using various proteases and both collision induced and electron transfer dissociation. ...
16-Apr-2008
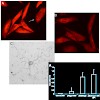
Antibodies against the neurite outgrowth inhibitor Nogo-A enhance axonal regeneration following spinal cord injury. However, antibodies directed against myelin components can also enhance CNS inflammation. The present study was designed to assess the efficacy of DNA vaccination for generating antibodies against Nogo-A and to study their pathogenic potential in a ...
16-Apr-2008
A few weeks ago, many of our friends suffered from ‘winter vomiting disease’, a form of gastroenteritis that swept epidemically across Germany. This unpleasant disease is caused by the highly contagious norovirus, a member of the Caliciviridae family of RNA viruses. Caliciviruses are unusual because they dock to sugar residues on the surfaces of cells to be ...
15-Apr-2008
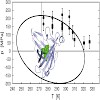
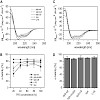
We have measured the equilibrium constant for the denaturation transition of the engineered fluorescein-binding lipocalin FluA as a function of pressure and temperature, taking advantage of the fact that the ligand’s fluorescence is almost fully quenched when complexed with the folded protein, but reversibly reappears on denaturation. From the equilibrium ...
12-Apr-2008
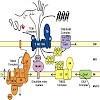
Biogenesis of mitochondria depends on the coordinated action of at least six protein translocases present in both mitochondrial membranes. They use different energy sources to drive unidirectional transport of proteins across and into mitochondrial membranes. Here we present an overview on the energetic requirements of different mitochondrial import pathways.
12-Apr-2008
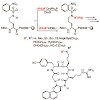
An optimized protocol for the mild and selective Fukuyama−Mitsunobu reaction was used for mono- and di-N-alkylation on solid support. Thereby, nonfunctionalized aliphatic and aromatic residues are quickly introduced into transiently protected, primary amines of a linear peptide. N-Alkylation can also be used to implement alkyl chains carrying (protected) ...
11-Apr-2008
The thiopeptide class of antibiotics targets the GTPase-associated center (GAC) of the ribosome to inhibit translation factor function. Using X-ray crystallography, we have determined the binding sites of thiostrepton (Thio), nosiheptide (Nosi), and micrococcin (Micro), on the Deinococcus radiodurans large ribosomal subunit. The thiopeptides, by binding within a ...
10-Apr-2008

Pathogenic bacteria often use effector molecules to increase virulence.vIn most cases, the mode of action of effectors remains unknown. Strains of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae (Pss) secrete syringolin A (SylA), a product of a mixed non-ribosomal peptide/polyketide synthetase, in planta1. Here we identify SylA as a virulence factor because a SylA-negative ...
09-Apr-2008
Evolution of multiresistant bacterial strains has meant that infectious diseases once again pose a major threat to public health. Since many antibiotics still target only a limited set of cellular functions, it is a desirable goal to expand the number and breadth of therapeutic targets as well as to gain a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms ...
04-Apr-2008
As a first approach to establishing a three-dimensional culture infection model, we studied the growth behavior of the extracellular pathogen Yersinia enterocolitica in three-dimensional collagen gels (3D-CoG). Surprisingly, we observed that plasmidless Y. enterocolitica was motile in the 3D-CoG in contrast to its growth in traditional motility agar at 37°C. ...
04-Apr-2008
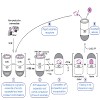
The GroEL/GroES chaperonin system mediates protein folding in the bacterial cytosol. Newly synthesized proteins reach GroEL via transfer from upstream chaperones such as DnaK/DnaJ (Hsp70).Here we employed single molecule and ensemble FRET to monitor the conformational transitions of amodel substrate as it proceeds along this chaperone pathway. We find that ...
02-Apr-2008
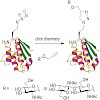
The importance of protein N terminus sequence composition for cell physiology was recognized more than two decades ago. However, its relevance for chemical protein engineering through an expanded genetic code was demonstrated only very recently. Nature changes the chemistry of the N terminus by posttranslational modifications (PTMs) such as longchain alkylation, ...
01-Apr-2008

Chromatin serves to package, protect and organize the complex eukaryotic genomes to assure their stable inheritance over many cell generations. At the same time, chromatin must be dynamic to allow continued use of DNA during a cell’s lifetime. One important principle that endows chromatin with flexibility involves ATPdependent ‘remodeling’ factors, which alter ...
28-Mar-2008
EH domains are protein–protein interaction domains that function in vesicular trafficking and endocytosis. Here, we report the NMR spectral assignments of the high-affinity complex between the second EH domain of Eps15 and a stonin 2 peptide—providing the basis for the characterization of a two-site binding mode.
21-Mar-2008
Heteronuclear residual dipolar one-bond couplings of organic molecules at natural abundance are most easily measured using t2 coupled HSQC spectra. However, inevitably mismatched transfer delays result in phase distortions due to residual dispersive antiphase coherences in such experiments. In this article, slightly modified t2 coupled HSQC experiments with clean ...
19-Mar-2008

CIPSM-Researchers Heinrich Leonhardt and Ulrich Rothbauer win the Binder-Innovation-Award for their work on the usage of fluorescent nano-antibodies to detect biological structures and processes in living cells. From left to right: Prof. Vestweber (President of the German Association of Cellbiology), Prof. Baumeister (MPI Martinsried), Dr. Ankerhold (Carl ...
19-Mar-2008

Ectodomain shedding of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by the two proteases alpha- and ß-secretase is a key regulatory event in the generation of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid ß peptide (Aß). ß-secretase catalyzes the first step in Aß-generation, whereas a-secretase cleaves within the Aß domain, prevents Aß generation and generates a secreted form of APP ...
14-Mar-2008
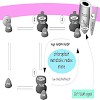
The preprotein translocon at the inner envelope of chloroplasts (Tic complex) facilitates the import of nuclear-encoded preproteins into the organelle. Seven distinct subunits have been identified so far. For each of those, specific functions have been proposed based on structural prediction or experimental evidence. Three of those subunits possess modules that ...
04-Mar-2008
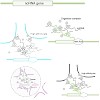
The combination of chromatin structure and the organization of chromosomes in eukaryotic nuclei affects many genome functions. Distinct functional states of genes ranging from ‘highly active’ to ‘silenced’ correlate with particular nucleosome arrangements, histone variants, histone modifications, and interactions of non-histone regulators. Transcription factors ...
03-Mar-2008

2008 is great! We are very happy that Dirk Trauner will join CIPSM and the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry of the LMU in August 08 as a newly established CIPSM full professor. Dirk's research centers on the total synthesis of complex natural products and rationally designed molecular probes and their application to biological problems, especially in ...
02-Mar-2008
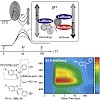
Hemithioindigo-molecules show a photochromic behavior due to a photo-induced Z/E-isomerization on a picosecond timescale. Changes in the reaction kinetics, caused by polar substituents attached to the thioindigo-moiety, are studied using time-resolved absorption spectroscopy. The experiments reveal that substituents in the thioindigo-part influence the reaction ...
01-Mar-2008
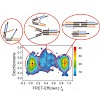
Bei PIE werden gepulste Anregungsquellen verwendet, wodurch die Information zugänglich ist, welche von ihnen für die Emission eines detektierten Photons verantwortlich war. Diese experimentell leicht zu installierende Technik bietet zahlreiche Vorteile, vor allem bei Untersuchungen an mehrfarbig markierten Molekülkomplexen. Beispielsweise besteht mit PIE die ...
01-Mar-2008

The etiologies of neurodegenerative diseases may be diverse; however, a common pathological denominator is the formation of aberrant protein conformers and the occurrence of pathognomonic proteinaceous deposits. Different approaches coming from neuropathology, genetics, animal modeling and biophysics have established a crucial role of protein misfolding in the ...
29-Feb-2008

NMR spectroscopy is a well-established technique for the screening of compound libraries. One of the biggest advantages of NMR spectroscopy in relation to other methods is that it directly detects even weakinteractions between ligand and target molecules, which makes it ideally suited for fragment-based ligand design. In addition, the number of false-positive ...
27-Feb-2008
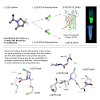
Proline residues affect protein folding and stability via cis/trans isomerization of peptide bonds and by the Cc-exo or -endo puckering of their pyrrolidine rings. Peptide bond conformation as well as puckering propensity can be manipulated by proper choice of ring substituents, e.g. Cc-fluorination. Synthetic chemistry has routinely exploited ringsubstituted ...
26-Feb-2008
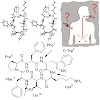
Full methyl jacket? A complete library of the N-methylated somatostatin cyclopeptidic analogue Veber–Hirschmann peptide cyclo(-PFwKTF-) is performed with the aim of improving its bioavailability. Several analogues from the library were found to bind to the somatostatin receptor in the nanomolar range and one of them shows a significant oral bioavailability of ...
22-Feb-2008
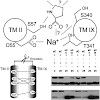
The Na+/solute symporter family comprises more than 400 members of pro- and eukaryotic origin. Using the Na+/proline transporter PutP of Escherichia coli as a model, the role of two conserved residues, Ser-340 and Thr-341, is investigated to obtain insights into the mechanism of transport catalyzed by members of this family. Substitution of these amino acids ...
19-Feb-2008
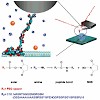
AFM-based single-molecule force spectroscopy has been used to study the effect of Hofmeister salts and protein hydrophobicity on the adhesion of recombinant spider silk proteins onto solid substrates. Therefore, a molecular probe consisting of a spider silk protein and an AFM tip has been developed, which (i) is a well-defined, small system that can be simulated ...
15-Feb-2008
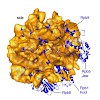
Related multisubunit RNA polymerases (RNAPs) carry out gene transcription in all kingdoms of life. Since structural information is limited to bacterial and eukaryotic RNAPs, we determined the cryo-electron microscopic structure of the RNAP from the thermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus at 13 Å resolution. Comparison with eukaryotic RNAP II reveals a conserved ...
13-Feb-2008

Bayer Schering Pharma (BSP) and CIPSM sign a strategic partnership. The aim of both partners is to initiate a scientific exchange and to carry out joint projects in the field of protein chemistry. With this cooperation the partners wish to simplify and essentially accelerate the transfer of fundamental perceptions into applications, in order to score a leading ...
12-Feb-2008

Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are a widespread and diverse class of molecular chaperones. In vivo, sHsps contribute to thermotolerance. Recent evidence suggests that their function in the cellular chaperone network is to maintain protein omeostasis by complexing a variety of non-native proteins. One of the most characteristic features of sHsps is their ...
11-Feb-2008
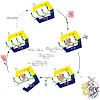
Remodelling protein nucleic acid interfaces is an important biological task, which is often carried out by nucleic acid stimulated ATPases of the Swi2/Snf2 superfamily. Here we study the mechano-chemical cycle of such an ATPase, namely the catalytic domain of the Sulfolobus solfataricus Rad54 homologue (SsoRad54cd), by means of fluorescence resonance energy ...
08-Feb-2008
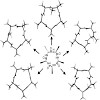
Systematic N-methylation of all peptide bonds in the cyclic pentapeptide cyclo(-d-Ala-Ala4-) has been performed yielding 30 different N-methylated derivatives, of which only seven displayed a single conformation on the NMR time scale. The conformation of these differentially N-methylated peptides was recently reported by us (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15 164–15 ...
08-Feb-2008

The ubiquitin-like SUMO system functions by a cyclic process of modification and demodification, and recent data suggest that the nucleolus is a site of sumoylation–desumoylation cycles.For example, the tumour suppressor ARF stimulates sumoylation of nucleolar proteins. Here, we show that the nucleolar SUMOspecific protease SENP3 is associated with nucleophosmin ...
07-Feb-2008
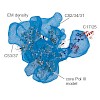
The eukaryotic RNA polymerases Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III are the central multiprotein machines that synthesize ribosomal, messenger, and transfer RNA, respectively. Here we provide a catalog of available structural information for these three enzymes. Most structural data have been accumulated for Pol II and its functional complexes. These studies have provided ...
06-Feb-2008
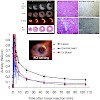
The purpose of this study was to determine the feasibility of a new positron emission tomography (PET) imaging approach using a 18F-labeled αvβ3 integrin antagonist (18F-Galacto-RGD) to monitor the integrin expression after myocardial infarction. METHODS: Male Wister rats were subjected to 20 min of transient left coronary artery occlusion followed by ...
06-Feb-2008

The linker histone H1 binds to the DNA in between adjacent nucleosomes and contributes to chromatin organization and transcriptional control. It is known that H1 carries diverse posttranslational modifications (PTMs), including phosphorylation, lysine methylation and ADP-ribosylation. Their biological functions, however, remain largely unclear. This is in part ...
05-Feb-2008
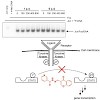
Molecular signals originating at the cell surface are conveyed by a complex system of interconnected signaling pathways to the nucleus. They converge at transcription factors, which in turn regulate the transcription of sets of genes which ultimately determine the cellular phenotype. Whereas enzymes involved in signaling pathways, that is, intracellular kinases ...
01-Feb-2008
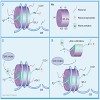
Many phenotypic changes of eukaryotic cells due to changes in gene expression depend on alterations in chromatin structure. Processes involved in the alteration of chromatin are diverse and include post-translational modifications of histone proteins, incorporation of specific histone variants, methylation of DNA and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. ...
01-Feb-2008

The active center clefts of RNA polymerase (RNAP) from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus (Pfu) and of yeast RNAP II are nearly identical, including four protruding loops, the lid, rudder, fork 1 and fork 2. Here we present a structure-function analysis of recombinant Pfu RNAP variants lacking these cleft loops, and analyze the function of each loop at different ...
01-Feb-2008
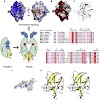
The ATPase RIG-I senses viral RNAs that contain 5`triphosphates in the cytoplasm. It initiates a signaling cascade that activates innate immune response by interferon and cytokine production, providing essential antiviral protection for the host. The mode of RNA 50-triphosphate sensing by RIG-I remains elusive. We show that the C-terminal regulatory domain RD of ...
01-Feb-2008
Since the discovery of radial glia as the source of neurons, their heterogeneity in regard to neurogenesis has been described by clonal and time-lapse analysis in vitro. However, the molecular determinants specifying neurogenic radial glia differently from radial glia that mostly self-renew remain ill-defined. Here, we isolated two radial glial subsets that ...
01-Feb-2008
Cells respond to a sudden increase in temperature with the transcription of a special set of genes, a phenomenon known as the heat shock response. In the yeast S. cerevisiae, the molecular chaperone Hsp26 is one component of the heat shock response. Hsp26 has the remarkable ability to sense increases in temperature directly and can switch from an inactive to a ...
01-Feb-2008
A combination of crystallography, biochemistry, and gene expression analysis identifies the coactivator subcomplex Med8C/18/20 as a functionally distinct submodule of the Mediator head module. Med8C forms a conserved α-helix that tethers Med18/20 to the Mediator. Deletion of Med8C in vivo results in dissociation of Med18/20 from Mediator and in loss of ...
23-Jan-2008
During the developmental formation of neuronal circuits, redundant synapses are eliminated and persisting synapses strengthened. In the immature cerebellum, climbing fiber–Purkinje cell synapses undergo a pronounced synaptic rewiring, from a multiple innervation around birth to a mono-innervation in adults. An early stage of this process consists in the ...
18-Jan-2008
DNA methyltransferases convert deoxycytidine (dC) nucleobases in DNA into 5-methyldeoxycytidines (dCMe) using the cofactor S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the methyl group donor.Methylation of the canonical dC base, particularly in gene promoter regions, induces complex processes, which finally lead to the silencing of the corresponding gene. This epigenetic gene ...
18-Jan-2008
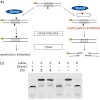
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b) is constitutively activated in many human tumors. Activity of STAT5b requires binding of its Src homology 2 (SH2) domain to certain phosphotyrosine-containing sequences. We have developed a highthroughput assay based on fluorescence polarization that allows screening of chemical libraries for compounds ...
18-Jan-2008
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b) is constitutively activated in many human tumors. Activity of STAT5b requires binding of its Src homology 2 (SH2) domain to certain phosphotyrosine-containing sequences. We have developed a highthroughput assay based on fluorescence polarization that allows screening of chemical libraries for compounds ...
17-Jan-2008
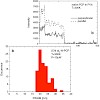
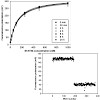
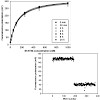
Single molecule spectroscopy was applied to study the optical properties of native and refolded peridinin–chlorophyll–protein (PCP) complexes. The native system is a trimer with six chlorophyll a (Chl a) molecules, while the refolded one contains two Chl a and resembles structurally and spectroscopically the PCP monomer. The fluorescence emission of single PCP ...
17-Jan-2008
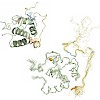
Eps15 homology (EH) domain-containing proteins play a key regulatory role in intracellular membrane trafficking and cell signalling. EH domains serve as interaction platforms for short peptide motifs comprising the residues NPF within natively unstructured regions of accessory proteins. The EH–NPF interactions described thus far are of very low affinity and ...
14-Jan-2008
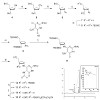
The oxidative DNA lesion, FaPydG rapidly anomerizes to form a mixture of the a and b anomer. To investigate the mutagenic potential of both forms, we prepared stabilized bioisosteric analogues of both configurational isomers and incorporated them into oligonucleotides. These were subsequently used for thermodynamic melting-point studies and for primerextension ...
09-Jan-2008
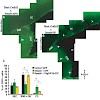
In the mammalian brain, neurogenesis continues only in few regions of the forebrain. The molecular signals governing neurogenesis in these unique neurogenic niches, however, are still ill defined. Here, we show that bone morphogenic protein (BMP)-mediated signaling is active in adult neural stem cells and is crucial to initiate the neurogenic lineage in the adult ...
09-Jan-2008
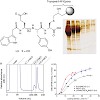
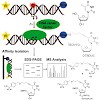
BACKGROUND: Hemophilia A is currently treated by infusions of the coagulation factor (F) VIII, of which production and purification remain a challenging task. Current purification procedures using immunoaffinity chromatography are cumbersome, expensive, and suffer from the instability of the applied antibody ligands, which elute along with the product and ...
08-Jan-2008

Single-pair fluorescence resonance energy transfer was used to track RNA exiting from RNA polymerase II (Pol II) in elongation complexes. Measuring the distance between the RNA 5´ end and three known locations within the elongation complex allows us determine its position by means of triangulation. RNA leaves the polymerase active center cleft via the previously ...
05-Jan-2008
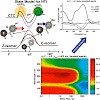
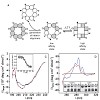
The photochemical reaction dynamics of a set of photochromic compounds based on thioindigo and stilbene molecular parts (hemithioindigos, HTI) are presented. Photochemical Z/E isomerization around the central double bond occurs with time constants of 216 ps (Z → E) and 10 ps (E → Z) for a 5-methyl-hemithioindigo. Chemical substitution on the stilbene moiety ...
03-Dec-2007
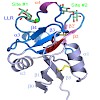
Langerin is a type II transmembrane oligosaccharide receptor on Langerhans cells (LCs), a prominent subclass of dendritic cells (DCs) that mediate immune responses in epithelia and play a role in HIV degradation. Its extracellular moiety comprises a neck region with several heptad repeats and an exposed carboxy-terminal calcium-type carbohydrate-recognition ...










